Kansai Science City Construction Promotion Office
Metropolitan Areas Development Office
City and Regional Development Bureau
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism


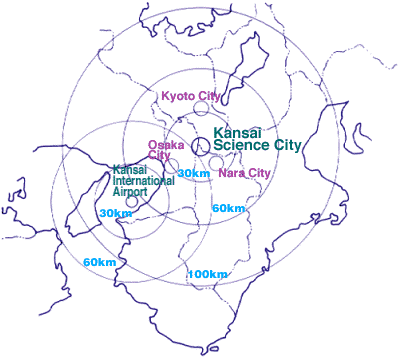 | # Location: | ||
| Keihanna Hill Area extending to the Left Bank of Kizu River and striding over Kyoto Prefecture, Osaka Prefecture and Nara Prefecture | |||
| Kyotanabe City, Kizugawa Town, Soraku-gun; Seika Town, | ||
| Hirakata City, Shijonawate City, Katano City | ||
| Nara City, Ikoma City | ||
| (Kansai Science City is located within the 30km radius from both central Osaka and central Kyoto.) | |||
| # Dimensions: | |||
| [ Kansai Science City ] | |||
| Approximately 15,000 ha | ||
| Approximately 410,000 | ||
 General Map of Kansai Science City General Map of Kansai Science City | [ Culture and Scientific Research Districts (12 places) ] | ||
| Approximately 3,600 ha | ||
| Approximately 210,000 | ||
| September 1978 | The Kansai Science City Study Committee (Chairman: Azuma Okuda, former President of Kyoto University); the "New City Project" was proposed. |
| June 1986 | Foundation of Kansai Research Institute was established. |
| June 1987 | The Kansai Science City Construction Act was issued and enacted. |
| September 1987 | The Prime Minister adopted "The Basic Policy on the Construction of Kansai Science City" (basic policy) in accordance with the Kansai Science City Construction Act. |
| March 1988 | "Construction Plan of Kansai Science City" (construction plan) furnished by the governors of the three prefectures (Kyoto, Osaka and Nara) concerned was approved. |
| August 1989 | Keihanna Interaction Plaza Incorporated was established. |
| July 1990 | Revision of "Construction Plan" of Nara Prefecture was approved. |
| January 1992 | Revision of "Construction Plan" of Kyoto Prefecture was approved. |
| April 1993 | Keihanna Plaza (the Facilities for Exchange of Culture, Scientific Studies and Research) was opened. (See photo) |
| Sep.-Nov. 1994 | Keihanna Science City Festival '94 was held. |
| April 1996 | The recommendations of the Kansai Science City Second Stage Plan Promotion Committee was submitted to the Prime Minister. ( future policies of Kansai Science City) |
| April 1997 | "The Basic Policy on the Construction of Kansai Science City" (basic policies) was revised. |
| July 1997 | Revision of "Construction Plan" of Nara Prefecture was approved |
| Oct 1999 | "The Basic Policy on the Construction of Kansai Science City" (basic policies) was revised again. |
| Completed and in operation | Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute International (ATR) | Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute International (ATR) | Seika - Nishi Kizu | Opened in April 1989 |
| Ion Engineering Center, Ion Engineering Research Institute | Ion Engineering Center and others | Himuro - Tsuda | Opened in July 1990 | |
| The Facilities for Exchange of Culture, Scientific Studies and Research "Keihanna Plaza" | Keihanna Interaction Plaza Incorporated | Seika - Nishi Kizu | Opened in April 1993 | |
| Nara Institute of Science and Technology | Government of Japan(Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology) | Takayama | Started enrollment in 1993 | |
| International Institute of Advanced Studies | Foundation of International Institute of Advanced Studies | Seika - Nishi Kizu | Opened in October 1993 | |
| Research Institute of Innovative Technology for the Earth (RITE) | Foundation of Research Institute of Innovative Technology for the Earth (RITE) | Seika - Nishi Kizu | Opened in November 1993 | |
| Nara Research Center of the Telecommunications Advancement Organization of Japan | Telecommunications Advancement Organization of Japan | Takayama | Opened in May 1995 | |
| Tsuda Science Core | Osaka Prefecture | Himuro - Tsuda | Opened in October 1995 | |
| Kyoto Prefectural Agricultural Resource Research Center | Kyoto Prefecture | Minami Tanabe - Komada | Opened in April 1997 | |
| Experimental Farm of Kyoto Prefectural University's Faculty of Agriculture | Kyoto Prefecture | Minami Tanabe - Komada | Opened in april 1997 | |
| Suzaku Gate | Government of Japan (Agency for Cultural Affairs) | Heijo Place Site | Opened in April 1998 | |
| Garden in the Eastern Palace | Government of Japan (Agency for Cultural Affairs) | Heijo Place Site | Opened in spring 1998 | |
| Suzaku Oji | Nara City | Heijo Place Site | Opened in March 1999 | |
| Advanced Photon Research Center | Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute | Kizu | Opened in September 1999 | |
| Communications Research Laboratory Keihanna Human Info-Communication Research Center | Government of Japan (Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications) | Seika - Nishi Kizu | Opened in July 2000 | |
| Special historical site "Heijo Palace Site" | Government of Japan (Agency for Cultural Affairs) | Heijo Place Site | Opened in April 2010 | |
| Kansai-kan(provisional name) of the National Diet Library | National Diet Library | Seika - Nishi Kizu | Opened in October 2002 |

Keihanna City
"Keihanna" refers to Kansai Science City,
as well as the hill on which the City's development is under way.
This logo symbolizes a flying angel,
who throws flowers from heaven,
while playing celestial music and burning incense.
The gentle curves comprising the logo represent
the gentle slopes of the Keihanna Hills.
At the same time, the three curves symbolize the past,
present and future; Kyoto, Osaka, Nara;
and the cooperation of industry,
academics, and the governments.
Kansai Science City Construction Promotion Office
Metropolitan Areas Development Office
City and Regional Development Bureau
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
at TEL: +81-3-5253-8111 (ext. 32-262) , FAX +81-3-5253-1586