Shinkansen Japanese High-speed rail
The Shinkansen is a high-speed rail that was pioneered in Japan. It has made a tremendous contribution to the development of Japan by connecting people, products, work and life. This is for people in the world involved with the planning and introduction of high-speed rail systems, with the purpose of describing and explaining the features and advantages of the Shinkansen system. It`s our hope that it can serve as helpful reference material to help in the creation of their own systems.

Absolute Reliability
The Shinkansen achieved both high safety and stability levels with its comprehensive technologies, which include vehicles, signals, and operating systems. They work together to create world-class safety.
Both Safe and Stable
Safety and stability are maintained by comprehensive technologies that encompass the performance of the carriages, control devices, and operating management systems.
ZERO 1964 ⇒ Present Time Safety
There have been no passenger fatalities since the Shinkansen first commenced operation in 1964. (Reference data: Total number of passengers from 1964 to 2009:Approx .9.2billion)
Within 1 Minute
Approximately 362,000 runs are made each year. The average delay time per trip is within one minute, even including weather-related delays.
Advanced Technologies
The Shinkansen boasts an impressive array of functions to meet diverse needs.
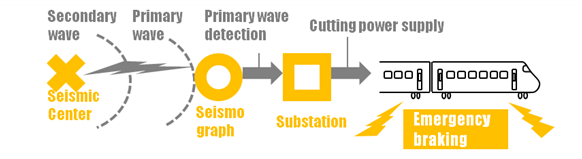
Early Earthquake Detection System
The system detects earthquakes at an early stage and immediately halts the trains. This technology was developed for one of the most earthquake-prone countries in the world.
Noise Control
The Shinkansen meets Japanese noise pollution standards-among the toughest in the world-with its pantograph, engineered carriage shape and light-weight carriages.
Connectivity with Existing Railways
The Shinkansen lines are linked directly to public transportation networks, offering even greater convenience and comfort.