Country Profile
Finland at the eastern end of Scandinavian Peninsula is a country of woods and lakes. Within the surface area of 338 thousand km², 74% of land area is covered with forest and lake area covers 32,000 km². The nation also includes more than 40 thousand islands off the southwest coast.
Major industry of Finland used to be wood-related such as papermaking and pulp, and metal, but since innovation industry such as electronics and ICT began to be the core driver of its economy in the late 1990s, modern and competitive economy developed and now the nation has grown to be one of the world's innovative leaders. Finland joined in the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union in 1999 as one of the precedent members.
TableFinland fast facts
| Country name | Republic of Finland |
|---|---|
| Surface area | 338 thousand km² (slightly smaller than Japan) |
| Population | About 5,490 thousand (2016) |
| Population density | 16/km² |
| Percentage of urban population | 84.2% (2015) |
| GDP | 299.6 billion dollars (2015: IMF) |
| GDP per capita | 41,973 dollars (2015: IMF) |
| Percentage of employment by industry | agriculture: 2.5% industry: 26.9% services: 70.6% (2016 est.) |
| GDP growth | 0.431% (2015: IMF) |
(Information Updated: March 2017)
FigureMap of Finland
Source: http://europa.eu/about-eu/countries/member-countries/finland/index_en.htm
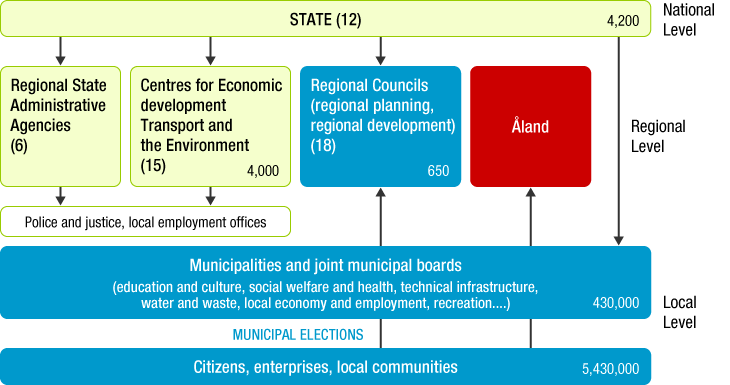
Local Administration System in Finland
Local administration system in Finland differs from other Scandinavian countries. It is single-layered and consisted of the central government and municipalities (kunta). However, for extensive areas, administration is implemented by outpost agencies and joint municipal boards (including Regional Councils stipulated in Act on Regional Development).
FigureLevels of public administration in Finland
Major Authorities Relating to Spatial Policy
| Name and Field of Plan/Policy | Organization | Web site |
|---|---|---|
| Regional Policy (overall) Rural Policy Committee, Islands Policy |
Ministry of Economic Affairs and Employment | https://tem.fi/en |
| Land Use Plan, Environmental Plan | Ministry of the Environment | http://www.ym.fi/en-us |
| Rural Policy | Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry | http://www.mmm.fi/en/index/ministry.html |
| Transport and Communication Policy | Ministry of Transport and Communications | https://www.lvm.fi/en/home |
| Regional-level economic, transport and environmental development | Centres for Economic Development , Transport and the Environment (ELY) : 15 on the main land |
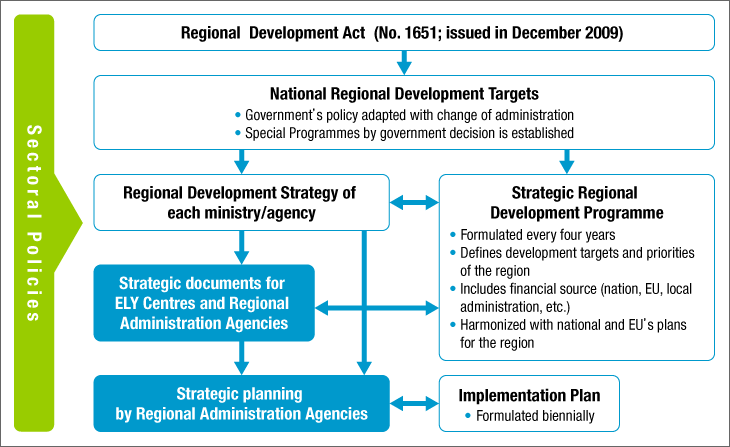
Plans and policies relating to national land and regional development
<System of national land policy>
As is the case with other European countries, Finland has no spatial plan for the whole country.
National land and regional policy is composed of regional development policy system as a socio-economic development plan and land use planning system as a spatial plan.
- Policy system of regional development
- <Laws and ordinances relating to regional development>
- -Act on regional development (No 1651/2009; issued on Dec.29, 2009)
- -Government Decree on regional development (1651/2009, issued on Dec.29, 2009)
FigureRegional Development Policy System
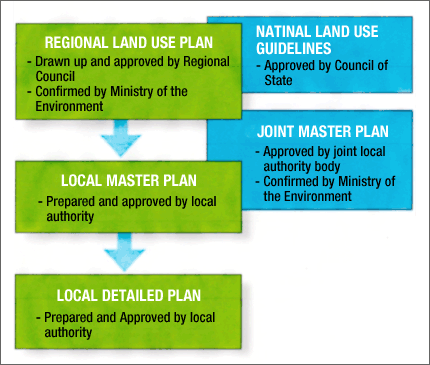
- Land use planning system
- Finland's land use planning system was revised over these several years (according to a literature written in 2011).
- Regional land use plan comply with Land-use and Building Act (132/1999)
FigureLand use system in Finland
Current Regional Policy
<Direction of Regional Policy>
Finland traditionally had a basic principle of treating inhabitants and others equally in providing services. Also there are region-specific characters and advantages. The nation is expected to prosper by making good use of those hereafter.
As is the case in Japan, ageing society is rapidly progressing in Finland. It is necessary to examine all kinds of countermeasures which will take in vitality of private companies and this is needed to be supported by regional policy. There is an intention of transferring the regionally specified structure of industry to a diversified industrial structure.
Change of system through transfer from vertically divided society to cross-sectional and horizontal society, and from top-down approach to bottom-up and customer-centered approach (for customers and inhabitants)to take in demands from lower-level.
Make digital technology utilized for rural-area promotion. In the future, by making use of information and communication network, enable administrative information to be retained in an optimum level --- efficiently by smaller number of people.
<Regional Innovation Measures>
The core organization responsible for research and innovation policy is Ministry of Education and Culture and Ministry of Employment and the Economy. Ministry of Education and Culture handles education, science policy, universities, higher education and Finland Academy. Ministry of Employment and the Economy handles the business related to industry/innovation policy, Tekes and VTT Technical Research Centre. About 85 % of the national research funds is spent by these two ministries.
Centre of Expertise Programme which started in 2002 is the core measure of regional innovation policy that plays an important role in the aspects of information and expertise within national growth strategy. This program gathers resources nationally, regionally and locally, exploits top-level expertise, underpins regional strength and expertise and deepens cooperative relations among the professional knowledge centers.
As of Centre of Expertise Programme 2007-2013, 13 national clusters were designated, which were implemented by 21 professional knowledge centers. The clusters and professional knowledge centers represent the highest expertise in each field of expertise.
Professional knowledge centers will implement projects through collaboration of research sector, educational institutions and business/industrial sector. These projects will enhance competitiveness of companies, strengthen and improve regional expertise, create new business and promote creation of new environment for innovation.
Centre of Expertise Programme has temporarily been stopped in 2013 due to the establishment of Katainen administration (National Coalition Party). (the programme sustained for 12 years)
Under the new administration, implementation of INKA (Innovative Cities programme) is centered by TEKES (Finnish Funding Agency for Innovation).
<Rural Policies>
95% of the national land of Finland is rural where 31% of the population lives.
In rural areas, out immigration to urban areas and ageing society is progressing rapidly.
It is important to continue providing appropriate services which will open the way to rural areas' employment.
Rural Policy Committee has been operating in Finland for 20 years. It was governed by Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry until 2 years ago but now the role is transferred to Ministry of Employment and the Economy. All of the ministries related to daily lives of the people are involved in rural policy. In deciding any of the matters, the administrative body must consider each rural area's characters and specialties.
Rural policy is divided into "broad" and "narrow" policies. Composition of narrow rural policy is mainly the assistance toward rural areas through EU Structural Reform Projects.
There are many organizations involved in rural policy. Rural Policy Committee functions as a body to implement concentrated and efficient rural policy.
<Policies for Disadvantaged Areas (Policies for Ethnic Minority "Sami")>
Ethnic Minority "Sami" (Laplanders) lives at the north of Finland. Today Sami parliament exists and they are guaranteed by the law.
Many inhabitable areas for Sami are designated. Although not a complete autonomy is guaranteed they can decide their language and culture on their free will.
On governmental implementation and enactment of laws, when it is expected to give any impact on the lives of Sami, it must be noticed to Sami parliament. For example, consultation is needed for land use, use of law-controlled preserved area and use of mineral resources.
Plan for Metropolitan Area (Helsinki)
| Name | Vision 2050 |
|---|---|
| Planning Period | - 2050 (Draft for 2015 will be finalized in December 2014) |
| Establishing Body | Helsinki City |
| Legal Placement | Master Plan complies with Land-use and Building Act (132/1999). There is no specific legal placement for Vision 2050. |
| Objective of the Plan and Development Strategy | <Seven Vision Themes> ①Helsinki is an Urban Metropolis Pulsating With Life, ②A City of Appealing Living Options, ③City of Economic Growth and Jobs, ④City of Sustainable Mobility, ⑤Recreation, Urban Nature and Cultural Environment, ⑥Helsinki's Seaside Areas, ⑦International Helsinki and Helsinki as Part of the Region <Urban Structure Model: The Rail Network City>
|
| About The Metropolitan Authority |
|
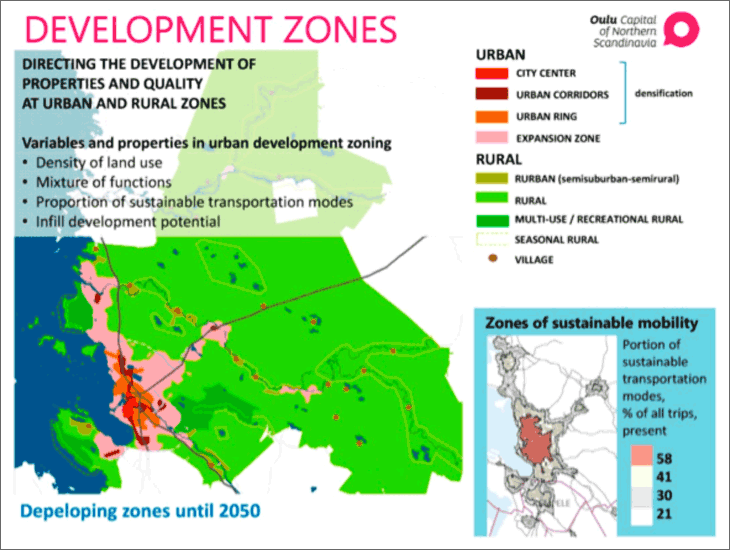
Plan of Local Central Urban Area (Oulu)
| Name | New Oulu Master Plan |
|---|---|
| Planning Period | -2050 (now being established) |
| Establishing Body | City of Oulu |
| Legal Base | Land-use and Building Act (132/1999) |
| Objective of the Plan and Development Strategy |
|
| Main Features |
|
Transnational and Extensive Issues on Spatial Policy
Formulation of open business platform (The Northern Growth Zone) is envisaged, which will be shared among the Balkan States including Russia. Finland is a crossover country of European communication and the great expectation of growth leads to the high regard of the concept.
Formulation of Barents Link is being under consideration which is a route of Atlantic Ocean - Finland - Siberia. It is intended to change the Europe - Far East course from the route via Suez Canal to the route connecting north end of Barents Sea and the Far East. If it succeeds, there is a chance for logistics upon Barents Sea route to become more active.
In relations with Japan, the route will correspond to Northern Sea Route.
Russia, having a vast national land, considers to strengthen partnership with areas around the border. In 2010, Russia designated an area called Euregio Karelia and examined about strenghening of partnership with Bosnia, North Bosnia, regional council of North Karelia and Kainuu. Upon achieving partnership with Russia, there are strategies such as preparation of border crossing and development of transport network, especially roads. As prioritized issues, there are; infrastructure development of border area and border crossing and attraction of Russian tourists.
(Information Updated: March 2015)
