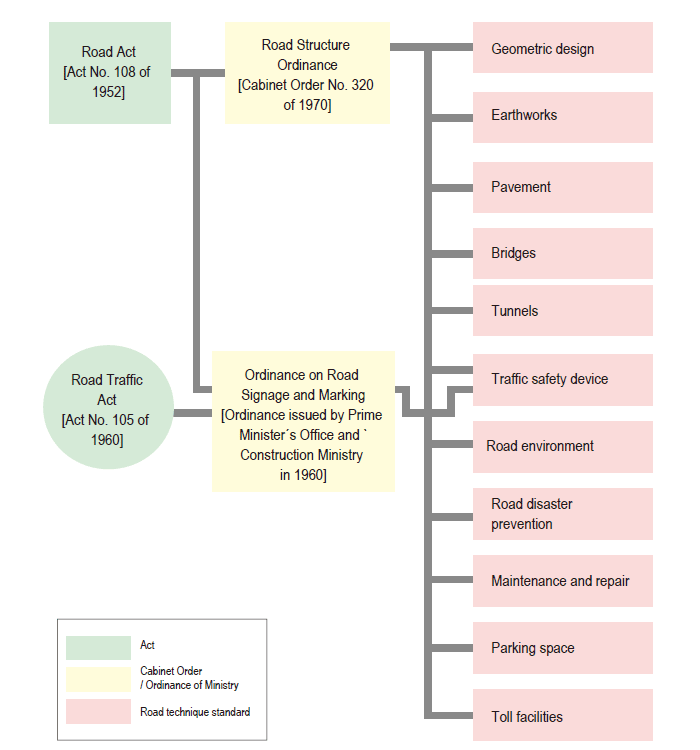
Technical standard
1. ROAD STRUCTURE ORDINANCE
(Government Ordinance No.320 of 29 October, 1970)
Structure of Road Technique Standards
(Purpose of This Ordinance)
Article 1
This Ordinance specifies general technical standards (limited to the provisions of the Road Act (hereinafter referred to as the "Act") Article 30.1.1, 30.1.3 and 30.1.12 for general technical standards of the structure of prefectural roads and municipal roads) for the structure of national expressways and national highways when these roads will be newly constructed or reconstructed and also specifies general technical standards that should be taken into account when technical standards (except for the provisions in Article 30.1.1, 30.1.3 and 30.1.12) for the construction of prefectural roads and municipal roads are required under the ordinances of prefectural or municipal governments, who also serve as a road administrator.
(Definition)
Article 2
The following terminology definitions shall apply to the corresponding terms in this Ordinance:
1. Sidewalk: A road section provided for dedicated pedestrian traffic, which is separated by curb lines or fences or other similar structures.
2. Bicycle track: A road section provided for dedicated bicycle traffic, which is separated by curb lines or fences or other similar structures.
3. Bicycle/pedestrian track: A road section provided for dedicated bicycle/pedestrian traffic, which is separated by curb lines or fences or other similar structures.
4. Carriageway: A road section used by dedicated vehicular traffic, except for bicycles.
5. Lane: A strip section of the carriageway (except for the service road) provided for safe and smooth traffic by directional separation of vehiculars traveling in a single direction.
6. Additional overtaking lane: An additional lane (except for climbing, turning and speed change lanes) provided specifically for vehicles to overtake other vehicles.
7. Climbing lane: A lane for slower vehicles to be separated from other vehicles on uphill roads.
8. Turning lane: A lane for vehicles to turn right or left.
9. Speed change lane: A lane for vehicles to accelerate or decelerate.
10. Median: A strip road section provided to separate a lane from the traffic in the opposite direction and ensure lateral clearances.
11. Service road: A strip of carriageway provided to applicable sections, parallel to the carriageway, to ensure access of vehicles to roadsides where access is prevented by embankment and/or cut, or other means.
12. Shoulder: A strip of road section connected with carriageway sidewalks, bicycle tracks or bicycle/pedestrian tracks to protect major road structure sections and to maintain carriageway functions.
13. Marginal strip: A strip section of the median or shoulder connected with the carriageway to provide optical guidance for drivers and ensure lateral clearance.
14. Stopping lane: A strip section of the carriageway principally used to park vehicles.
15. Bicycle traffic lane: A strip section of the carriageway provided for safe and smooth passage of bicycles.
16. Track bed: A road section dedicated for use by streetcar traffic (streetcars as specified in Article 2.1.13 of the Road Traffic Act [Act No.105 of 1960]; this definition of streetcars shall apply hereinafter).
17. Island: An area facility provided at intersections, carriageway separation points, bus bays, streetcars stops, or other areas to ensure safe and smooth vehicular traffic or the safety of pedestrians crossing streets or bus and streetcar passengers boarding or alighting.
18. Planted strip: A strip of road section provided for tree planting in order to improve road traffic environment and ensure a better living environment along roadsides, which is separated by using curb lines or fences or other similar structures.
19. On-street facility: A road accessory facility on sidewalks, bicycle tracks, bicycle/pedestrian tracks, median, shoulders, bicycle paths and bicycle/pedestrian paths, except for common ducts and common cable ducts.
20. Urban area: An area forming or expected to form a city or town.
21. Rural area: Other areas than urban areas.
22. Design traffic volume: Daily vehicular traffic volume determined by planners for road construction or reconstruction planners designated by the Land, Infrastructure and Transport Ministry's ordinance according to requirements in the same ordinance for the basis of road design, in consideration of trends of development in the area and vehicular traffic conditions in the future.
23. Design speed: Vehicle speed that is used as a basis for road design.
24. Sight distance: The distance measured along the lane (or carriageway (except for bicycle traffic lanes) in the case of a road without a lane and the same is applied hereinafter) centerline at which an apex of a 10cm high object on the lane centerline is visible from 1.2m on the lane centerline.
(Road Classification)
Article 3
1. Roads shall be classified into Types 1 through 4 as listed in the following table.
| Area where road is located
National expressways and access-controlled highways or other roads.
| Rural Area | Urban Area |
| National expressways and access-controlled highways | Type1 | Type2 |
| Other Roads | Type3 | Type4 |
2. Type 1 roads shall be classified into classes 1 through 4 as listed in Table 1, Type 2 roads shall be classified into Class 1 or 2 as listed in Table 2, Type 3 roads shall be classified into classes 1 through 5 as listed in Table 3, and Type 4 roads shall be classified into classes 1 through 4 except where topographic conditions or other circumstances do not permit such provision. Roads can be classified into one class lower than the original class unless roads are otherwise applicable to Type 1 Class 4, Type 2 Class 3, Type 3 Class 5, or Type 4 Class 4.
Table 1 Type 1 Roads
| Road type | Topography area where road is located | Designed daily volume (vehicles/day) | |||
| More than 30,000 | 20,000~ 30,000 | 10,000~ 20,000 | Less than 10,000 | ||
| National Expressway | Level Area | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | |
| Mountainous Area | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 | ||
| Roads other than National Expressway | Level Area | Class 2 | Class 3 | ||
| Mountainous Area | Class 3 | Class 4 | |||
Table 2 Type 2 Roads
| Area where road is located
Road type
| Areas other than Central Business District | Central Business District |
| National Expressway | Class 1 | |
| Roads other than National Expressway | Class 1 | Class 2 |
Table 3 Type 3 Roads
| Road type | Area where road is located | Designed daily volume (vehicles/day) | ||||
| More than 20,000 | 4,000~ 20,000 | 1,500~ 4,000 | 500~ 1,500 | Less than 500 | ||
| National Highway | Level Area | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | ||
| Mountainous Area | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 | |||
| Prefectural Roads | Level Area | Class 2 | Class 3 | |||
| Mountainous Area | Class 3 | Class 4 | ||||
| Municipal Roads | Level Area | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 | Class 5 | |
| Mountainous Area | Class 3 | Class 4 | Class 5 | |||
Table 4 Type 4 Roads
| Designed daily volume (vehicles/day)
Road type
| More than 10,000 | 4,000 ~ 10,000 | 500 ~ 4,000 | Less than 500 |
| National Highway | Class 1 | Class 2 | ||
| Prefectural Roads | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | |
| Municipal Roads | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 |
3. Roads shall be classified as specified in the previous paragraph 2 based on traffic conditions.
4. Type 1, 2 and 3 Class 1 through 4 roads or Type 4 Class 1 through 3 roads (limited to elevated roads and other structures from which vehicles cannot access roadsides for Type 3 Class 1 through 4 roads and Type 4 Class 1 through 3 roads) can be specified as the roads provided exclusively for the traffic of smaller motor vehicles (hereinafter indicating small-sized vehicles and other similar small vehicles; and pedestrians and bicycles in the case of Type 3 Class 1 through 4 and Type 4 Class 1 through 3 roads), in an unavoidable case such as for a topographical reason and due to conditions of urbanization, there shall be a neighboring detour road for other types of vehicles, other than smaller motor vehicles.
5. A lane specifically for the traffic of smaller motor vehicles can be provided, by separating other lanes on Type 1, 2 and 3 Class 1 through 4 roads or Type 4 Class 1 through 3 roads, in unavoidable cases such as for a topographical reason and due to conditions of urbanization. In the case of Type 3 Class 1 through 4 roads and Type 4 Class 1 through 3 roads, the lane specifically for the traffic of smaller motor vehicles shall be limited to elevated roads or other structures from which vehicles cannot access roadsides.
6. Roads shall be classified into smaller motor vehicle roads (hereinafter indicating the roads provided specifically for the traffic of smaller motor vehicles specified in the paragraph 4 and smaller motor vehicles and pedestrians and bicycles in Type 3 Class 1 through 4 and Type 4 Class 1 through 3 roads and vehicles specified in the previous paragraph) and regular motor vehicle roads (hereinafter indicating roads and road sections other than smaller motor vehicle roads).
(General Technical Standards for Construction of National Expressways and National Highways Structures)
Article 3-2
The next Article through Article 40 specify general technical standards for the construction of national expressways and national highways structures, when these roads will be newly constructed or reconstructed.
(Design Vehicles)
Article 4
1. Roads shall be so designed for the safe and smooth passage of small-sized motor vehicles and semitrailers (hereinafter indicated combined body consisting of trailing motor vehicle and trailed vehicle without front axle, in which a part of the trailed vehicle rests on the motor vehicle and substantial weight of the trailed vehicle and its load are supported by the motor vehicle) on Type 1, Type 2, Type 3 Class 1 or Type 4 Class 1 regular motor vehicle roads, or regular motor vehicle roads that are designated as the primary highway freight network (hereinafter indicated the primary highway freight network as specified in Road Act Article 48.17.1; this definition of the primary highway freight network shall apply), small-sized motor vehicles and regular-sized motor vehicles on other regular motor vehicle roads and smaller motor vehicles on smaller motor vehicle roads).
2. Specifications for the vehicle that is a basis of road design (hereinafter referred to as “design vehicle”) by Type shall be listed below.
| Length | Width | Height | Front-edge overhang | Wheelbase | Rear-edge overhang | Minimum t urning radius | |
| Small-sized motor vehicle | 4.7 | 1.7 | 2.0 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 1.2 | 6.0 |
| Smaller motor vehicles | 6.0 | 2.0 | 2.8 | 1.0 | 3.7 | 1.3 | 7.0 |
| Regular-sized motor vehicle | 12.0 | 2.5 | 3.8 | 1.5 | 6.5 | 4.0 | 12.0 |
| Semi-trailer | 16.5 | 2.5 | 3.8 (4.1 in the case of regular motor vehicle roads that are the primary highway freight network) | 1.3 | Front section wheelbase: 4.0 Rear section wheelbase: 9.0 | 2.2 | 12.0 |
For this table, the following terminology definitions shall apply to the corresponding terms.
1. Front-edge overhang: Distance from the front face of the vehicle body to the center of the front-wheel axle of a vehicle.
2. Wheelbase: Distance from the center of front-wheel axle of a vehicle to the center of the rear-wheel axle.
3. Rear-edge overhang: Distance from the rear face of the vehicle body to the center of the rear-wheel axle of a vehicle.
(Lanes)
Article 5
1. The carriageway (except for the service roads, stopping lanes,bicycle traffic lanes and other sections specified by the ordinances of Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism) shall consist of the below-specified lanes, except for those classified as Type 3 Class 5.
2. The number of lanes shall be 2 (except for additional overtaking, climbing, turning and speed change lanes and the same is applied in the following paragraph) in accordance with the road classification and on rural roads where design daily traffic volume is no more than values of standard design volume (hereinafter indicating maximum allowable traffic volume) as listed in the following table, while taking into account topographic conditions.
| Classification | Topography | Standard Design Volume (vehicles/day) | |
| Type1 | Class 2 | Level Area | 14,000 |
| Class 3 | Level Area | 14,000 | |
| Mountainous Area | 10,000 | ||
| Class 4 | Level Area | 13,000 | |
| Mountainous Area | 9,000 | ||
| Type3 | Class 2 | Level Area | 9,000 |
| Class 3 | Level Area | 8,000 | |
| Mountainous Area | 6,000 | ||
| Class 4 | Level Area | 8,000 | |
| Mountainous Area | 6,000 | ||
| Type4 | Class 1 | 12,000 | |
| Class 2 | 10,000 | ||
| Class 3 | 9,000 | ||
As for Type 4 roads with many intersections, standard design traffic volume shall be calculated by multiplying standard design traffic volume herein by 0.8.
3. The number of lanes on roads, other than those specified in the provision above, (except for Type 2 one-way roads and Type 3 Class 5) shall be more than 4 (a multiple of 2 unless otherwise required depending on traffic conditions) on Type 2 roads and one-way roads shall be more than 2 on roads that meet the road classification and are located in rural areas, and shall be determined by the rate of design daily traffic volume on the road according to standard design daily traffic volume per lane as listed in the following table, taking into consideration topographic conditions.
| Classification | Topography | Standard Design daily Traffic Volume per Lane(vehicles/lane/day) | |
| Type1 | Class 1 | Level Area | 12,000 |
| Class 2 | Level Area | 12,000 | |
| Mountainous Area | 9,000 | ||
| Class 3 | Level Area | 11,000 | |
| Mountainous Area | 8,000 | ||
| Class 4 | Level Area | 11,000 | |
| Mountainous Area | 8,000 | ||
| Type2 | Class 1 | 18,000 | |
| Class 2 | 17,000 | ||
| Type3 | Class 1 | Level Area | 11,000 |
| Class 2 | Level Area | 9,000 | |
| Class 3 | Mountainous Area | 7,000 | |
| Level Area | 8,000 | ||
| Class 4 | Mountainous Area | 6,000 | |
| Mountainous Area | 5,000 | ||
| Type4 | Class 1 | 12,000 | |
| Class 2 | 10,000 | ||
| Class 3 | 10,000 | ||
In the case of Type 4 roads with many intersections, standard design traffic volume per lane shall be calculated by multiplying standard design traffic volume per lane herein by 0.6.
4. Lane width (except for climbing, turning, and speed change lanes,) shall be the as listed in the columns for lane width, in the following table, in accordance with road classification. However, the lane width on Type 1 Class 1 and 2 or Type 3 Class 2 or Type 4 Class 1 regular motor vehicle roads may add 0.25m to the values as listed in the columns depending on the traffic situation. Lane width on Type 1 Class 2 or 3 smaller motor vehicle roads or Type2 Class 1 roads may be reduced 0.25m from the values as listed in the columns in unavoidable cases, such as for topographical and other reasons.
| Classification | Lane Width (m) | ||
| Type1 | Class 1 | 3.5 | |
| Class 2 | |||
| Class 3 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 3.5 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 3.25 | ||
| Class 4 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 3.25 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 3.0 | ||
| Type2 | Class 1 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 3.5 |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 3.25 | ||
| Class 2 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 3.25 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 3.0 | ||
| Type3 | Class 1 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 3.5 |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 3.0 | ||
| Class 2 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 3.25 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 2.75 | ||
| Class 3 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 3.0 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 3.0 | ||
| Class 4 | 2.75 | ||
| Type4 | Class 1 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 2.75 |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 3.25 | ||
| Class 2 and 3 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 2.75 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 2.75 | ||
5. Carriageway width on Type 3 Class 5 regular motor vehicle roads (except for bicycle traffic lanes) shall be 4m. However, the width could be reduced to 3m where design daily traffic volume is extremely low and topographic conditions or special reasons do not permit such provisions or where a narrow pass is created on regular motor vehicle roads pursuant to the provisions of Article 31.2.
(Lane Division)
Article 6
1. The lanes (hereinafter this applies for all except one-way roads) on Type 1, Type 2 or Type 3 Class 1 roads shall be directionally divided. It is also applied to other roads with four or more lanes if necessary for safe and smooth traffic.
2. Notwithstanding the provisions of the first sentence of the preceding paragraph, Type 1 roads with three or less lanes (hereinafter, this applies for all except for climbing, turning and speed change lanes) may be left directionally undivided in unavoidable cases, such as for topographical conditions or any other reasons.
3. A center strip shall be provided, when required, for directional lane division.
4. Center strip width shall be no less than the values indicated in the left columns in the following table. However, the center strip width can be reduced to values listed in the right columns, in the same table, where tunnels longer than 100m, bridges longer than 50m, elevated roads, topographic conditions or other special conditions do not permit.
| Classification | Center Strip Width(m) | ||
| Type1 | Class 1 | 4.5 | 2.0 |
| Class 2 | |||
| Class 3 | 3.0 | 1.5 | |
| Class 4 | |||
| Type2 | Class 1 | 2.25 | 1.5 |
| Class 2 | 1.75 | 1.25 | |
| Type3 | Class 1 | 1.75 | 1.0 |
| Class 2 | |||
| Class 3 | |||
| Class 4 | |||
| Type4 | Class 1 | 1.0 | |
| Class 2 | |||
| Class 3 | |||
5. A marginal strip shall be provided to the center strip.
6. The width of the marginal strips shall be the values listed in the left column of the following table in accordance with road classification. However, the center strip width can be reduced to the values listed in the right columns of the same table when the center strip width of the road or road section is reduced in accordance with paragraph 4.
| Classification | Width of Marginal Strip Provided to Center Strip(m) | ||
| Type1 | Class 1 | 0.75 | 0.25 |
| Class 2 | |||
| Class 3 | 0.5 | ||
| Class 4 | |||
| Type2 | 0.5 | 0.25 | |
| Type3 | Class 1 | 0.25 | |
| Class 2 | |||
| Class 3 | |||
| Class 4 | |||
| Type4 | Class 1 | 0.25 | |
| Class 2 | |||
| Class 3 | |||
7. Fences, or other similar structures, or curb lines connected to the marginal strip shall be provided to sections other than the marginal strip of the center strip (hereinafter referred to as the "median").
8. When on-street facilities are provided on the median, the center strip width shall be determined considering clearances as specified in Article 12.
9. If necessary, additional overtaking lanes shall be provided to the carriageway of Type 1 roads with single lanes in each direction.
(Service Roads)
Article 7
1. The service roads shall be provided to Type 3 or 4 roads with more than four lanes (except for climbing, turning and speed change lanes) if necessary.
2. Service road (except for bicycle traffic lanes) width shall be a standard 4m.
(Shoulders)
Article 8
1. Shoulders shall be provided to roads connected to carriageways, except where a center strip or stopping lane is provided.
2. Shoulder width on the left side of the carriageway shall be, in accordance with road classification, no less than the values listed in the left column of the following table. However, road width may be reduced to the values listed in the right columns in the same table where additional overtaking lanes, climbing lanes or speed change lanes are provided, or on road sections of bridges 50m or longer or elevated roads or other road sections in unavoidable cases such as for a topographical or other special reasons.
| Classification | Width of Shoulder Provided on Left of Carriageway(m) | |||
| Type1 | Class 1 and 2 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 2.5 | 1.75 |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 1.25 | |||
| Class 3 and 4 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 1.75 | 1.25 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 1.0 | |||
| Type2 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 1.25 | ||
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 1.0 | |||
| Type3 | Class 1 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 1.25 | 0.75 |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 0.75 | |||
| Class 2 through 4 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 0.75 | 0.5 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 0.5 | |||
| Class 5 | 0.5 | |||
| Type4 | 0.5 | |||
3. Notwithstanding the provisions of the preceding paragraph, shoulder width on the left side of carriageways on Type 1 roads with directionally divided lanes shall be, in accordance with road classification, no less than the values listed in the left column of the following table. However, shoulder width on the left side of the carriageway may be reduced to the values listed in the right columns in the same table where the road section is in a tunnel of no shorter than 100m, on bridges of no shorter than 50m, on elevated roads with low traffic volume of larger vehicles, or in unavoidable conditions such as for topographic or other reasons.
| Classification | Width of Shoulder Provided on Left of Carriageway(m) | ||
| Class 2 and 3 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 2.5 | 1.75 |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 1.25 | ||
| Class 4 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 2.5 | 2.0 |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 1.25 | ||
4. Width of the shoulders provided on the right of carriageway shall be, in accordance with road classification, no less than the values listed in the right column of the following table.
| Classification | Width of Shoulder Provided on Right of Carriageway(m) | ||
| Type 1 | Class 1 and 2 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 1.25 |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 0.75 | ||
| Class 3 and 4 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 0.75 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 0.5 | ||
| Type 2 | Regular motor vehicle roads | 0.75 | |
| Smaller motor vehicle roads | 0.5 | ||
| Type 3 | 0.5 | ||
| Type 4 | 0.5 | ||
5. Shoulder widths of the regular motor vehicle roads in tunnels (except for shoulders specified in the paragraph 3) or shoulder widths on the left side of smaller motor vehicle roads (except for shoulders specified in the paragraph 3) may be reduced to 1m on Type 1 Class 1 or 2 roads, 0.75m on Type 1 Class 3 or 4 roads and 0.5m on Type 3 (except for Class 5) regular motor vehicle roads or Type 3 Class 1 smaller motor vehicle roads.
6. As for the shoulder connecting to the service road, values of "1.25" and "0.75" in the left column of Type 3 carriageway as tabulated in Section 2 shall be regarded as "0.5" and provisory requirements in Section 2 shall not be applied.
7. On roads where sidewalks, bicycle tracks or bicycle/pedestrian tracks are provided, major road structures shall be protected. If smooth carriageway traffic can be maintained, the shoulder connecting width can be omitted or the width can be reduced.
8. A marginal strip shall be provided to the shoulder connecting with the carriageway on Type 1 or 2 roads.
9. The width of the marginal strips for regular motor vehicle roads shall be the values listed in the left column of the following table in accordance with road classification. The width of the marginal strips on smaller motor vehicle roads shall be 0.25m. However, shoulder widths for the regular motor vehicle roads in tunnels may be the values listed in the right columns in the same table.
| Classification | Width of Marginal Strip Provided to Shoulder (m) | ||
| Type1 | Class 1 | 0.75 | 0.5 |
| Class 2 | |||
| Class 3 | 0.5 | 0.25 | |
| Class 4 | |||
| Type2 | Class 1 | 0.5 | |
| Class 2 | |||
10. Where it is necessary to protect major road structures, the shoulder shall be provided on road ends so as to be connected to the sidewalk, bicycle track or bicycle/pedestrian track.
11. Where on-street facilities are provided on the shoulder connected to the carriageway, shoulder width shall be the values of shoulder width provided for the left side of the carriageway listed in paragraph 2 or the values of shoulder width provided for the right side of the carriageway listed in paragraph 4, plus the values required for the on-street facilities.
(Stopping Lanes)
Article 9
1. A stopping lane shall be provided on the left carriageway end on Type 4 roads to prevent stopping vehicles from impeding safe and smooth traffic.
2. The stopping lane width shall be 2.5m. However, the width may be reduced to 1.5m where the traffic volume of larger vehicles is low.
(Bicycle Traffic Lanes)
Article 9-2
1. Bicycle traffic lanes shall be provided on the extreme left of carriageways (for roads where a stopping lane is provided, the right side of the stopping lane; the same shall apply in the following paragraph) on Type 3 or 4 roads with higher vehicle and bicycle traffic volume (except for roads to which bicycle tracks are provided), except where topographic conditions or other special reasons do not permit such provision.
2. Bicycle traffic lanes shall be provided on the left carriageway end on Type 3 or 4 roads with higher bicycle traffic volume or Type 3 or 4 roads with higher vehicle and pedestrian traffic volume (except for roads to which bicycle tracks are provided and roads specified in the preceding paragraph) if separation of bicycle traffic is considered necessary for safe and smooth traffic, except where topographic conditions or other special reasons do not permit such provision.
3. Bicycle traffic lanes shall be wider than 1.5m, except where topographic conditions or other special reasons do not permit such provision, in such cases the width can be reduced to 1m.
4. Bicycle traffic lane width shall be determined in consideration of bicycle traffic conditions on roads.
(Track Bed)
Article 9-3
The track bed width shall be, in accordance with single or double track, wider than the values listed in the bottom columns of the following table.
| Single or Double Track | Track Bed Width(m) |
| Single Track | 3 |
| Double Track | 6 |
(Bicycle Track)
Article 10
1. Bicycle tracks shall be provided on both sides of roads on Type 3 (except for Class 4 and 5; the same shall apply in the following paragraph) or 4 (except for Class 3; the same shall apply in this paragraph) roads with higher vehicle and bicycle traffic volume,where the design speed is 60km/h or more, except where topographic conditions or other special reasons do not permit such provision.
2. Bicycle tracks shall be provided on both sides of the roads to ensure safe and smooth traffic on Type 3 or 4 roads with higher bicycle traffic volume or on Type 3 or 4 roads with higher vehicle and pedestrian traffic volume (except for roads specified in the preceding paragraph), if separation of bicycle traffic is considered necessary, except where topographic conditions or other special reasons do not permit such provision.
3. Bicycle tracks shall be wider than 2m, except where topographic conditions or other special reasons do not permit such provision, in such cases the width can be reduced to 1.5m.
4. Where on-street facilities are provided on the bicycle tracks, the road width shall be determined in consideration of clearances as specified in Article 12.
5. Bicycle track width shall be determined in consideration of bicycle traffic conditions on roads.
(Bicycle/Pedestrian Track)
Article 10-2
1. Bicycle/pedestrian tracks shall be provided on both sides of Type 3 or 4 roads with large traffic volume (except for roads where the bicycle tracks or bicycle traffic lanes would already be provided) except where topographic conditions or other special reasons do not permit such provisions.
2. Bicycle/pedestrian track width shall be wider than 4m for roads with higher pedestrian traffic volume and wider than 3m for other roads.
3. Where pedestrian bridges or pedestrian underpasses (hereinafter referred to as “pedestrian bridges etc.”) or on-street facilities are provided, the bicycle/pedestrian track width shall be increased by 3m where pedestrian bridges etc. are to be constructed, 2m where a roofed bench is to be installed, 1.5m where a row of trees is to be planted, 1m where a bench is installed or 0.5m in other cases, respectively to the values given in the preceding paragraph., The requirements as specified above shall be applied except for Type 3 Class 5 roads where topographic conditions or other special reasons do not permit such provisions.
4. The bicycle/pedestrian track width shall be determined in consideration of bicycle and pedestrian traffic conditions on the road.
