Systematization of Resource/Energy Recycling
- Today, the scarcity in resources and energy on a world level and the apparent global warming are becoming major issues. The transition to a recycling society and the establishment of a low carbon society is necessary. Also, transition to a recycling system that utilizes and regenerates collected substances as resources and energy is necessary from a temporary system that excludes and processes the existing sewage.
- The sewage system discharges massive amount of greenhouse gas along with the processing of sewage and dirt. However, it also has a potential as a great energy source. According to the Kyoto Protocol Target Achievement Plan (determined within the cabinet in March 2008), when it is compared to situations when the countermeasures take place, a difference can be seen in the reduction of greenhouse gas of approximately 2.16 million (approx. 30%) tons by 2010 of which energy reduction, new energy countermeasure 900 thousand tons and high temperature combustion of sewer sludge 1.26 million tons.
- Support for specific engagements including the diffusion and promotion of new technology for high temperature burning of sewer sludge, energy reduction in sewage facilities, creation of fuel from sewer sludge, and introduction of sunlight/micro hydro power generation.
- In addition to this, regarding phosphorus which is a valuable resource included in the sewage, since the price of fertilizers is rising within the country because of reasons such as the shortage of phosphorus on a world-wide scale, the collection and application of phosphorus is requested from sewer sludge. The promotion of engagements that use and collect phosphorus is implemented in collaboration with the relative ministries and agencies including the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries.
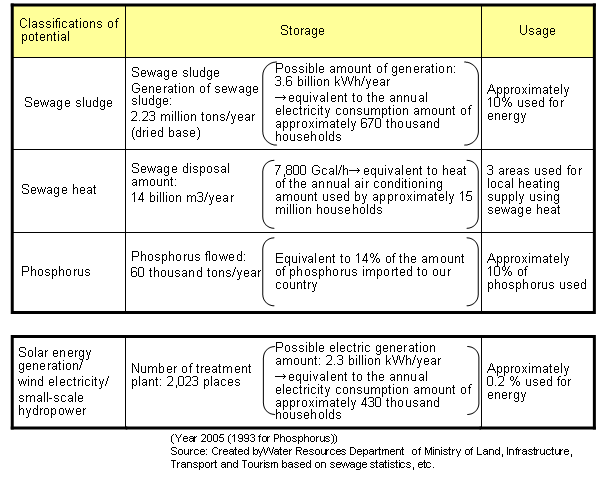
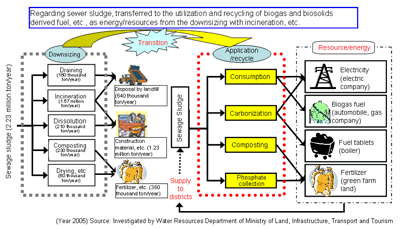
Condition of resource/energy use in sewer system
- The sewer system collects heat and sewage water that generates from city activities and holds great resource and energy potential but its usage is still low.
Condition of resource/energy use in sewer system
Usage of sewage sludge
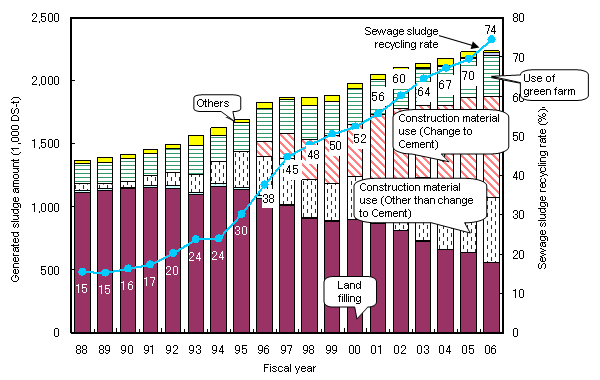
- The material use of sewage sludge is steadily developing and even though it has reached approximately 70%, use of organic matter within the sewage sludge as energy/resource is limited.
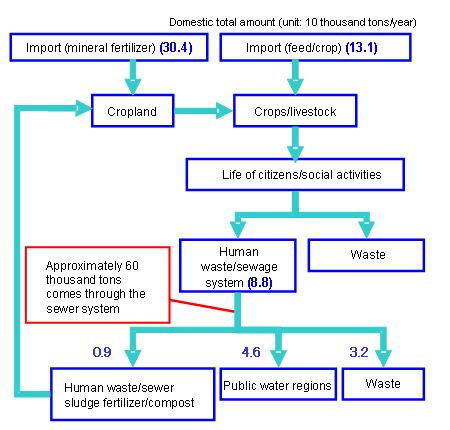
- Within the sewage, 14% of the imported amount of phosphorus flows in, but it is only limited to 10% for its use as compost.
Transition of material use
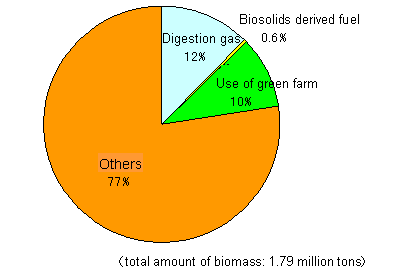
Use of biomass within sewage sludge (Year 2006)
Approx. 14 % of imported amount of phosphorus comes through the sewer system
Ideal future sewage system toward the formation of the recycling society
- In addition to the sewage system, promotion of engagements that collaborate and cooperate with related major organizations, such as for the supply of resources and energy to districts in collaboration with other fields and other businesses is taking place.
Ideal future sewage system toward the formation of the recycling societyüi
Closed up imageüj
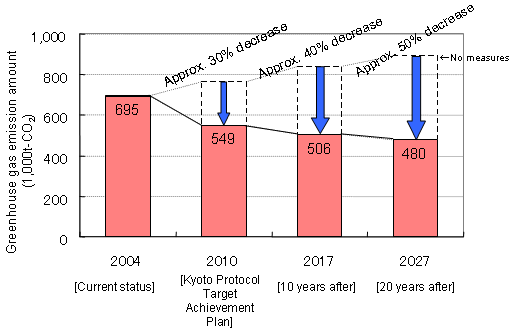
Possible amount of reduction of greenhouse effect gas within the sewage system
Calculation of the reduction amount of greenhouse effect gas 10 years and 20 years from now. When it is compared to cases where reduction of green house effect gas does not take place,
- Approximately 40 % cutback in the year 2017 (Cutback of approx. 3.4 million t of CO2)
- Approx. 50 % cutback in the year 2027 (Cutback of approx. 4.1 million t of CO2 üj
ü”Estimation of possible amount of the reduction of greenhouse gas using the presently available technology based on a fixed assumption
üiCalculated by the ügGreenhouse effect prevention committee in sewageühüj
Possible amount of reduction of greenhouse effect gas within the sewage system
Specific engagements and effects
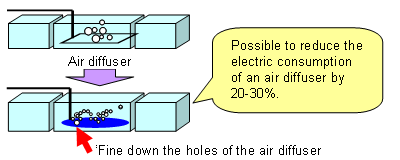
ć@Countermeasures for energy saving in sewage facilities
üEBy making an air diffuser that generates the necessary air for organism processing also generate micro foam, it will become easy for oxygen to dissolve and it becomes possible to cut back the electricity consumption of the air diffuser (which takes most of the electricity at the work site) by 20 - 30 %.
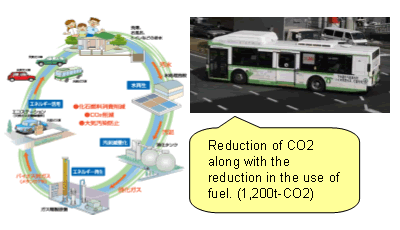
ćACountermeasures toward new energy in sewage
üEIn collaboration with the transport department, sewage-created bio gas is supplied for energy used by natural gas automobiles. (Kobe City)
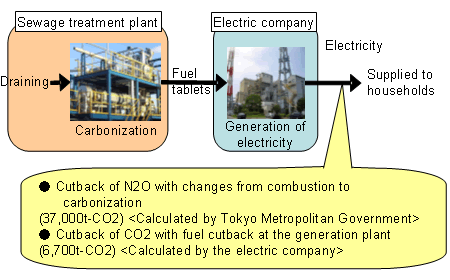
üEIn collaboration with the electric company, carbonized Derived Fuel is used as a fuel for substituting coal at the heat power plant.
(Tokyo Metropolitan Governmentü©JOBAN JOINT POWER CO., LTD üj
üEMicro hydro power generation using the effluent differences of sewage treatment water, and wind power generation and solar power generation using sewage facilities.
ćBCountermeasures for reduction of dinitrogen monoxide üiN2Oüj
Upgrading the combustion in the influidized incineratorüiraising the combustion temperature from 800üÄ to 850üÄüjcan reduce approximately 60% of N2O that holds a green house effect 310 times that of CO2.
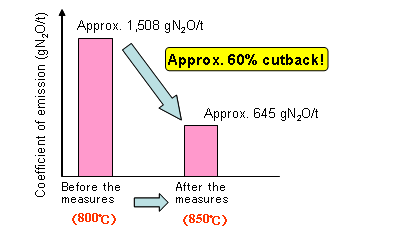
Comparison before and after the measures of fluidized incinerator