 |
 |
A basic role of sewerage is to eliminate
rainwater (so-called "internal water")
that has fallen in cities |
 |
Encouragement of hard and soft countermeasures
in order to protect people's lives, property,
and urban functions from frequent urban flood damage |
 |
Infrastructure target: percentage of achievement
of urban anti-flood measures: 52% (2004) >
54% (2007)
No. of households that need emergency resolution in case of flooding
to floor level: 74,000 households (2004) >
60,000 (2007) |
|
 |
Internal water countermeasures
are one role of the sewerage |
|
Flood damage caused
by inability of sewerage and rivers to drain rain that has fallen
 internal
water flood damage internal
water flood damage |
|
 |
Proportion of damage
by internal water |
|
| Total of decade from 1994
to 2003 (from flood damage statistics) |
 |
Tokyo flood damage
(2004) |
|
 |
Vicinity of a reservoir
intersection that caused road flooding
(Typhoon 22) |
|
 |
 |
Factors that intensify
flood damage in cities |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Increase of localized
torrential downpours in recent years |
|
 |
Change of rain runoff
before and after urban development |
|
| Before development,
rainwater was seeping underground. Due to development, the earth's
surface was covered with concrete, etc., resulting in frequent flooding
when large quantities flow in a short timeFlood damage caused by |
|
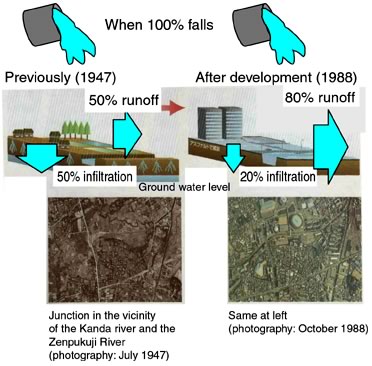 |
| (an example in a Tokyo
ward) |
|
 |
Increase of flood
damage in underground facilities |
|
 |
| 2003 Fukuoka City |
 |
| 1999 Tokyo |
|
 |
 |
| 1999 Fukuoka City
(fatalities) |
|
|
 |
 |
Comprehensive anti-flood
measure by sewerage |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Minimization
of damage by encouraging software and self-help |
| Goal
of minimizing damage by encouraging self-help
while limiting districts and time-periods and pushing forward
steadily with effective hardware countermeasures.
Moreover, reinforcing software countermeasures
paves the way for effective self-help. |
|
|
| Effective hardware
countermeasures |
Installation and operation of efficient,
priority-focused facilities
 |
Active introduction of reservoir / infiltration
facilities |
 |
Effective use of existing facilities
Networking of main line pipes and drains
Real-time control |
|
| Reinforcement of
software countermeasures |
Encouragement of information-gathering
and -provision in support of self-help
 |
Assistance to encourage self-help |
 |
Publication of internal waters hazard
maps |
 |
Promotion of provision of real-time information
Use of rain radar and fiber optic
|
 |
Carry out training regarding floods and
disseminate information |
|
| Encouragement of
self-help |
Minimization of the damage by encouragement
of self-help
 |
Setup of water stops in underground facilities |
 |
Setup of sandbags when flooding occurs |
 |
Setup of storage infiltration facilities,
etc. |
|
|