 |
| Hokkaido
Comprehensive Development Promotion |
|
| The Significance of the Development
of Hokkaido |
Because of difference in climate
and culture from the main island of Honshu, many citizens of Japan have
strong affection for Hokkaido and consider it to be a unique area.
The development of Hokkaido was slow. Only after the Meiji Period
did Japan seriously promote the development of Hokkaido by introducing projects
and large-scale development of nationally owned land using the latest technology
and ideas, resulting in the evolution of a pioneer endeavor entrusted with
the dreams of the future of Japan. Today Hokkaido continues to attract millions
of people as the land of hope.
In addition,
| · |
Possessing approximately one-fourth of
the arable land of Japan, anyone would agree that Hokkaido holds a
valuable role as the nation's food base both in the present and in
the future. |
| · |
Positioned at a nodal point between North
America, Europe and East Asia, and very close to the far eastern area
of the Russian Federation which has developed international resources
and energy, Hokkaido has a position of advantage in promoting international
exchange. |
| · |
With population density approximating
that of a small European country, Hokkaido has wide land space making
it capable of using this land to cope with economic and social changes,
and when compared to other areas, a much higher capability by developing
and using (natural) resources. |
| · |
Blessed by a rich natural environment
distinctive of the North, Hokkaido is a land formed by beautiful,
majestic agricultural landscapes. All of these features combine to
provide Hokkaido with characteristics and individuality not found
in other areas. |
On the other hand, with the advent of globalization we are confronted
with such issues as global environmental problems escalate and if we close
our eyes to them, not only will it bring about diversification of citizen's
lifestyle, we can expect to be confronted with sudden population decrease
and an aging population combined with a diminishing number of children.
Under such conditions, Hokkaido with its land, nature, customs and geographical
conditions will have a great advantage:
| · |
Steadily providing safe food resources |
| · |
Contributing to problem solutions by maintaining
natural environment, resources and energy |
| · |
Providing living space for citizens' self
realization and interaction through tourism, rest and recreation,
etc. |
| · |
Offering a base for international learning
exchange |
In such ways, it is hoped that Hokkaido will play a central
role. By so doing, Hokkaido can provide a working model for other areas
or act in place of other areas that are not able to do so and take the lead
in directing our country in the right direction.
For this reason it has become necessary for Hokkaido to contribute
to the solution of the country's problems and fully fulfill the role expected
of it by promoting comprehensive development. |
| The Road to the Development
of Hokkaido |
The first pioneers came to Hokkaido
in 1869 and, except for a brief period when three prefectures were under
one bureau, development continued until the end of the Second World War
under a one-dimensional government policy of organizational control.
| · |
1869: |
The new Meiji government established a
development mission |
| · |
1882: |
The development mission was disbanded
and three prefectures, Hakodate, Sapporo and Nemuro were established |
| · |
1883: |
The Department of Agriculture and Commerce
established the Hokkaido Project Management Bureau |
| · |
1886: |
The three prefectures and the Hokkaido
Project Management Bureau were disbanded and the Hokkaido Government
(as a state organization) was established |
After the war (WWII), along with the enactment of the Hokkaido
Development Act, the Hokkaido Development Authority, Hokkaido Development
Bureau and Hokkaido Development Finance Public Corporation were set up and
once again the development of Hokkaido was promoted under a unique system.
| · |
1947: |
By action of a local government act, the
Hokkaido Government was abolished and Hokkaido (as a regional entity)
was established |
| · |
1950: |
The Hokkaido Development Law was passed
and Hokkaido Development Authority established |
| · |
1951: |
Established Hokkaido Development Bureau
in Sapporo |
| · |
1956: |
Established Hokkaido Development Finance
Public Corporation (In the following year, 1957, this was reorganized
as Hokkaido-Tohoku Development Finance Public Corporation) |
| · |
1999: |
Established the Development Bank of Japan
(a merger with Hokkaido-Tohoku Development Finance Public Corporation) |
After that, connected with the reorganization of government
ministry, the Hokkaido Development Authority was transferred to the Ministry
of Land, Infrastructure and Transport which took over its duties and administrative
functions.
| · |
January 2001: |
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and
Transport was established. |
|
| Features of Hokkaido Development
Structure |
Based on the Hokkaido Development
Act, the Hokkaido comprehensive development is promoted by the national
government following the characteristics of the region.
The promotion structure of the Hokkaido development administration
has the following characteristics.
 |
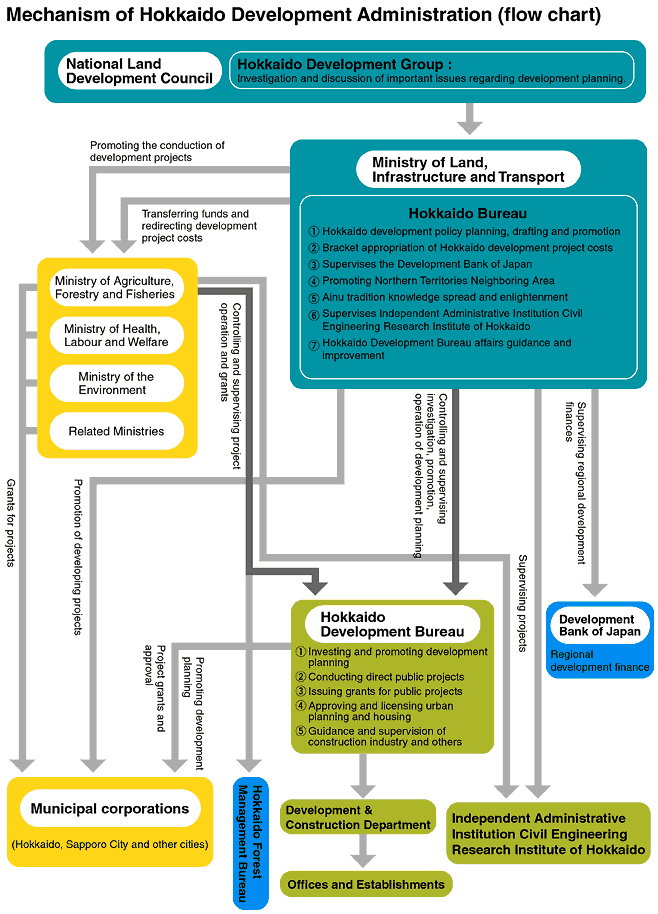
A Hokkaido Bureau in charge of Hokkaido
development was established in the main office of the Ministry of
Land, Infrastructure and Transport, which in turn created the Hokkaido
Development Department, a local branch to conduct Hokkaido development
projects.
 Development
of Hokkaido Bureau under the Hokkaido Development Bureau structure
administration is developed to conform to actual local conditions Development
of Hokkaido Bureau under the Hokkaido Development Bureau structure
administration is developed to conform to actual local conditions
|
 |
For closer alignment and coordination
between the Hokkaido Bureau, as central, and relevant ministries and
bureaus
 Development
of integrated administration, from the establishment of the Hokkaido
comprehensive development planning to the implementation of projects
based on these plans Development
of integrated administration, from the establishment of the Hokkaido
comprehensive development planning to the implementation of projects
based on these plans |
 |
Hokkaido Development Bureau, besides instigating
direct public projects as those conducted by Honshu and other district
regional development departments and regional agricultural administration
offices, undertook administering grants, urban and housing administration,
and the advancement of construction industry.
 One-dimensional
direct enterprises, direct public projects and unified comprehensive
subsidized projects. One-dimensional
direct enterprises, direct public projects and unified comprehensive
subsidized projects. |
 |
Actively promoting the growth and development
of industry through regional development financing from the Development
Bank of Japan.
 The
Development Bank of Japan promotes comprehensive industrial promotion
and industrial infrastructure development through the Hokkaido Development
Bureau. The
Development Bank of Japan promotes comprehensive industrial promotion
and industrial infrastructure development through the Hokkaido Development
Bureau. |
|
 |
| Evolving New Hokkaido Development |
In terms of nature, geography,
society and economy, the basis of the Hokkaido Development Administration
plan has an attraction that differs greatly from those of other areas of
Japan. The policy decided upon is how Hokkaido by contributing to the development
of our country expects to develop and preserve itself, adjusting from the
viewpoint of the nation as well as the area, aiming at realizing this goal
through the cooperation of government and private sectors.
In accordance with this point of view, as specified in the Hokkaido
Development Act, Article 2, Section 1: "From the beginning of fiscal
year 1951, the country shall establish a Hokkaido comprehensive development
plan and based on this shall undertake projects in accordance with legal
regulations governing such enterprises," and it is expected that the
country itself will plan and carry out the development of Hokkaido.
For the realization of the goal of Hokkaido contributing to
the development of our country, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and
Transport, which has established the development of Hokkaido as one of its
major administrative functions, is promoting positive measures to respond
to the various requirements of the new age. |
|