What is the Expressway Numbering System?
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) is introducing this new numbering system, a scheme that combines route numbers with route names, to Japan’s growing expressway network in order to make it easier to understand for all expressway users, including foreign visitors to Japan.
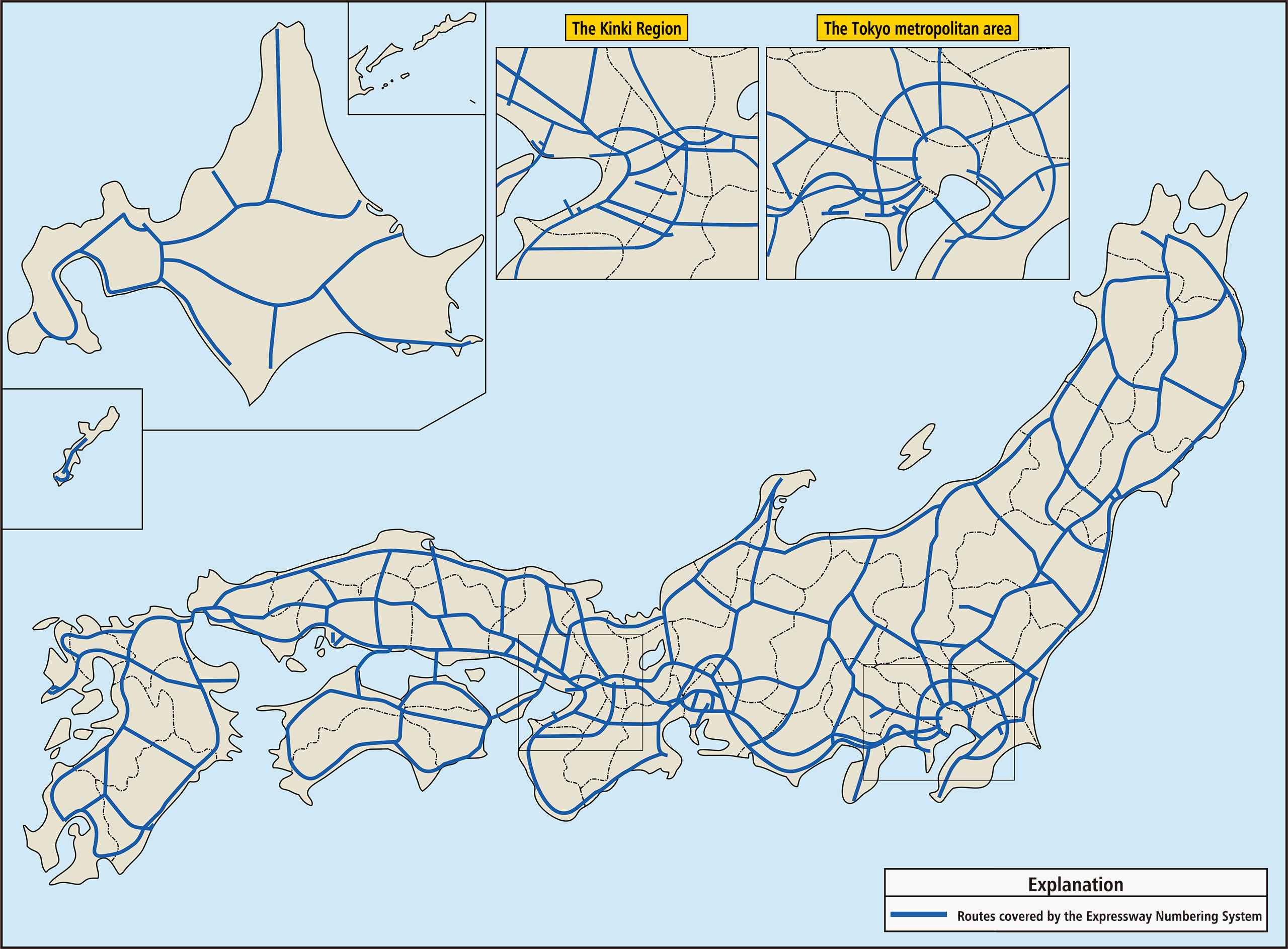
Routes covered by the Expressway Numbering System
〇 Routes forming the arterial high-standard highway network (“national expressways” and “national highways for motor vehicles only”) as well as regional expressway networks that supplement this network
〇 Routes forming expressway networks that provide access to major airports, harbors, and tourist areas from the arterial high-standard highway network
(*Urban expressways that are already numbered [e.g., the Tokyo Metropolitan Expressway, Hanshin Expressway, etc.] are excluded from the new Expressway Numbering System.)
Description of Expressway Numbering
Basic features of the Expressway Numbering System
1.It’s easy to get used to.
●The system uses the national route numbers (one or two digits) of main national routes that are already familiar to local residents.
2.It’s simple and easy to understand.
●As a rule, numbers are limited to one or two digits.
●Routes having similar functions (for example, they have the same start and end points) are grouped into route “families.”
●Road types and functions are indicated with alphabetic letters.
・The letter “E” appearing at the beginning of a number indicates an expressway.
・The letter “A” appearing at the end of a route number indicates a grouped route (i.e., road in a route family).
・The letter “C” appearing at the beginning of a route number indicates a circular route.
3.It represents the structural layout of the nation.
●It establishes route “start” and “end” points to allow representation of the nation’s structural layout using major expressway numbers.
Specific numbering classifications
| (1) Route that runs parallel to a single- or double-digit national highway | The number of the national highway is assigned to the route. | Examples: *The parallel route is National Route 1. |
|---|---|---|
| (2) Route that is grouped with (i.e., is in the same “family” as) a single-digit national highway | The Shin-Tomei Expressway and Shin-Meishin Expressway, which run parallel to the Tomei Expressway and Meishin Expressway (both “1”), respectively, are grouped with those expressways with the number “1A.” Similarly, the Chugoku Expressway, which runs parallel to the Sanyo Expressway (“2”), is grouped with that expressway with the number “2A.” |  Shin-Tomei Expressway Shin-Meishin Expressway Isewangan Expressway |
 Chugoku Expressway Kanmon Expressway |
||
| In the cases of routes “3,” “4,” and “5,” the number is assigned to the route that was built first. Newer sections that run parallel to the existing national highway are grouped with that national highway with the letter “A.” |   〔Hachinohe Expressway, Aomori Expressway〕  〔Sasson Expressway〕 |
|
| (3) Circular route | Circular routes in the Tokyo and Nagoya metropolitan areas have their function indicated with the alphabetic letter “C.” Numbers are assigned with consideration for consistency with other existing urban expressway circular routes. |      |
| (4) Route numbered by collectively viewing routes that run parallel to a single- or double-digit national highway as one | The Hokkaido Junkan Expressway is assigned the number “5” because it is part of the main expressway layout of the nation and Hokkaido. |  〔Hokkaido Expressway, etc.〕 (National Routes 5, 37, 36, 12, and 40) |
| Routes that generally match the direction of a double-digit national route within the same region are given the number of that national route. | Examples:  |
|
| If the parallel national highway has a three-digit number or is a route in which the national highway route number of the parallel national highway is assigned to another route, and there is an adjacent national highway, the relevant national route number is extended. | Examples: Futtsu-Tateyama Road (National Routes 14, 16, and 127) |
|
| (5) Other route | Other routes are numbered with a double-digit number of 59 or higher that is not already in use as a national highway number. | Example: |
Route symbol design and how to read route numbers
Route symbol design
The design uses a compact format to present route numbers as functionally as possible.
○Single-digit number

Tomei Expressway
Meishin Expressway

Shin-Tomei Expressway
Shin-Meishin Expressway
Isewangan Expressway
○Double-digit number

Chuo Expressway (Takaido - Okaya)

Shikoku Odan Expressway
(Kochi - Ozu)
〔Kochi Expressway, etc.〕
Matsuyama Expressway (Ozu - Matsuyama)
○Circular route

Metropolitan Inter-City Expressway (Ken-O Expressway)
(Kamariya - Kisarazu)

Tokyo Wan Aqua-Line
Aqua Renraku Expressway
How to read route numbers
| Route number | Japanese reading | English reading |
|---|---|---|
| E1 | E-ichi | E-one |
| E4A | E-yon-A | E-four-A |
| E56 | E-goju-roku | E-fifty-six |
| C4 | C-yon | C-four |
| CA | C-A | CA |
Road sign guidance
Signs show both route numbers and route names.
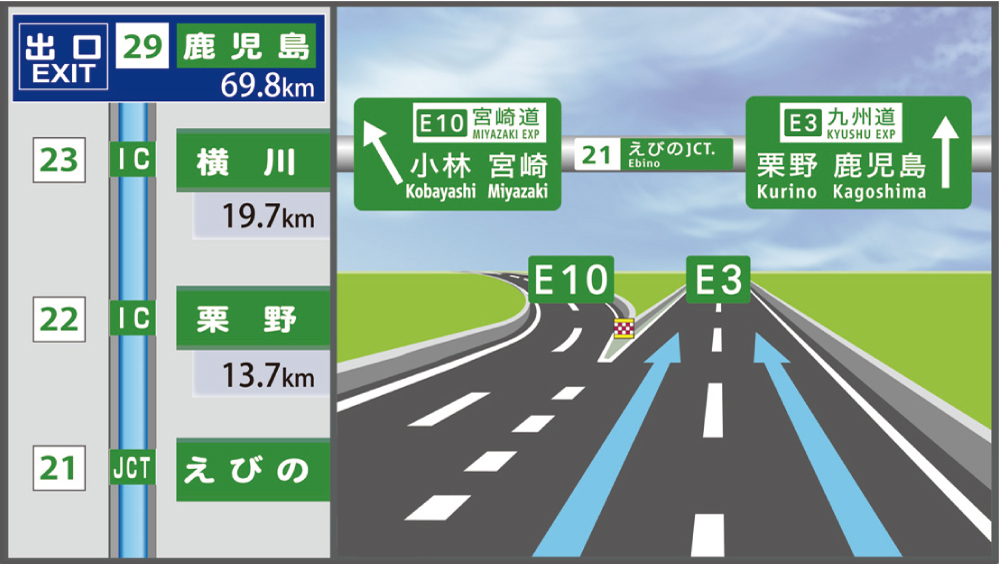
Examples of signs at expressway entrances
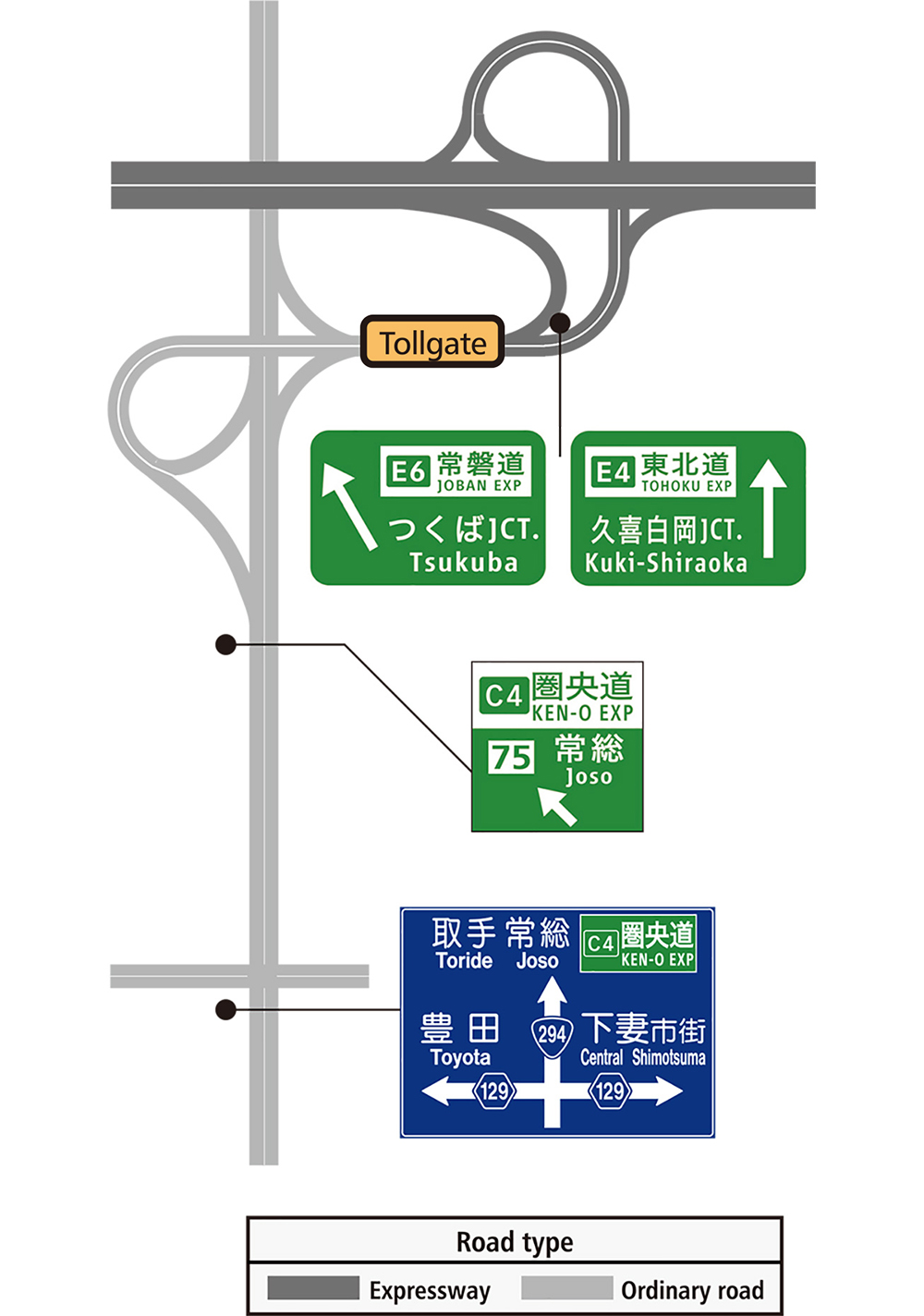
Examples of signs at junctions
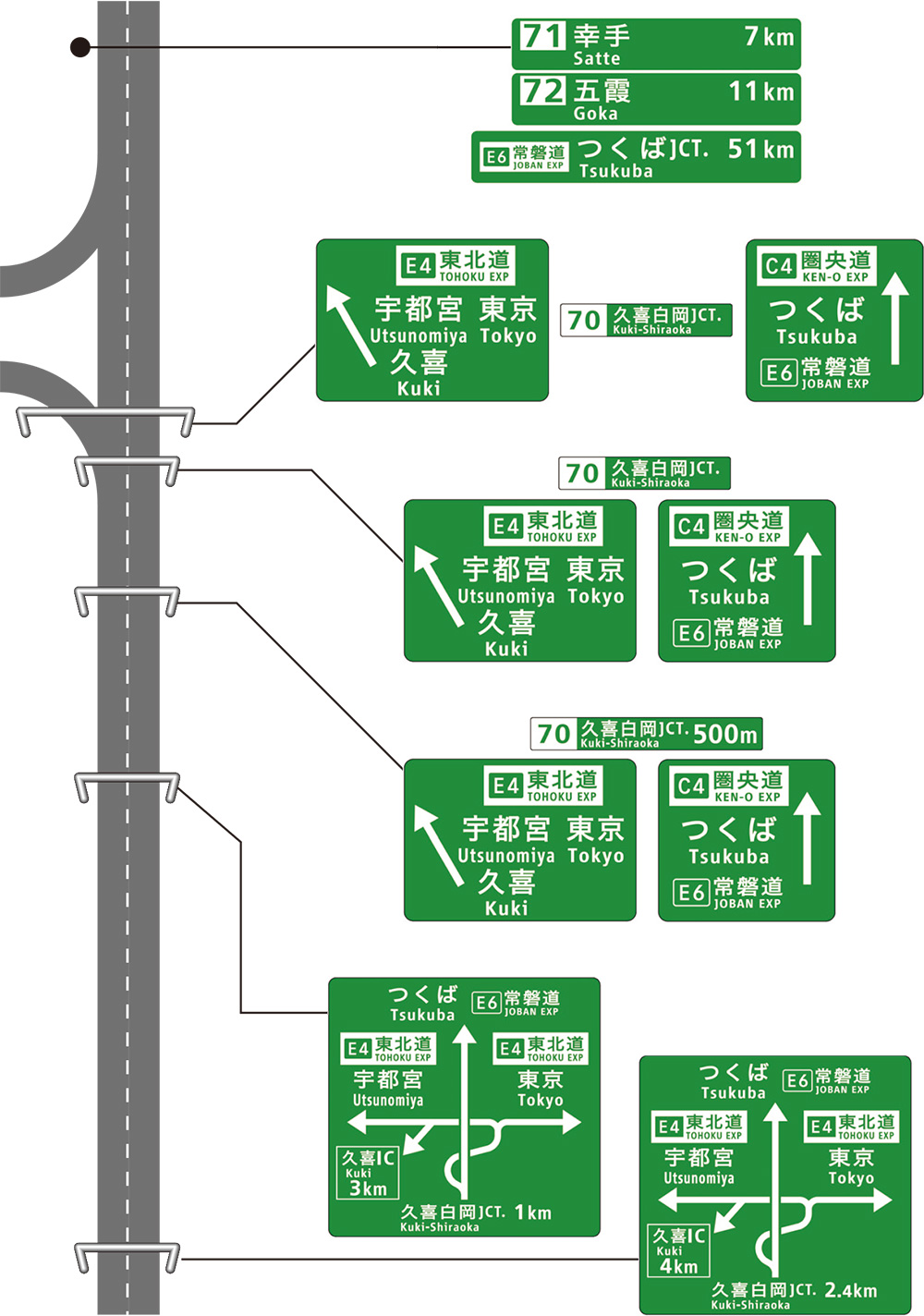
Application of expressway numbering
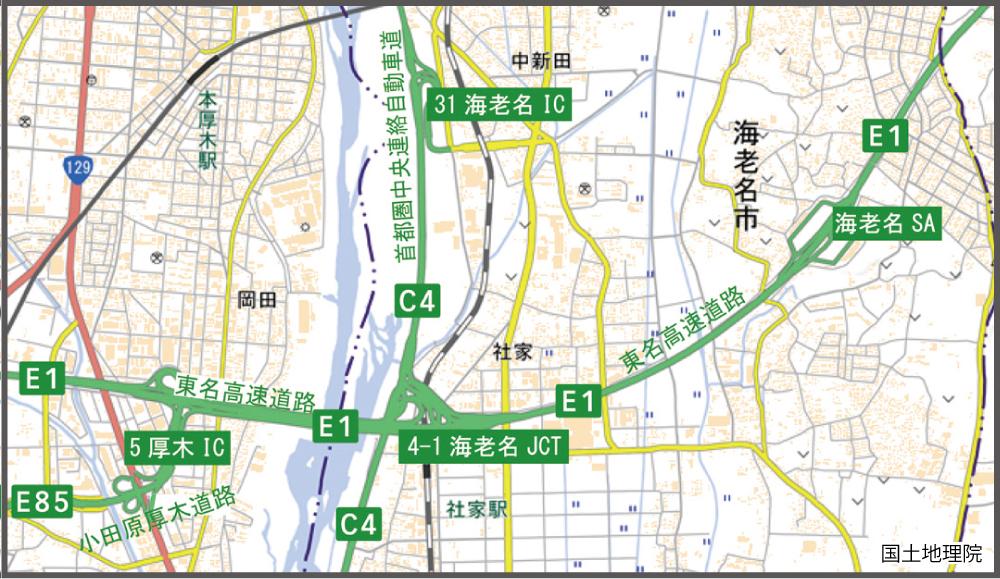
The Expressway Numbering System is being applied to maps, car navigation systems, and various other tools and media.
Example of numbering on a map
Example of numbering in a navigation system