| |
 |
| |
 |
| |
 |
Method of promoting the Plan |
| 1. Diverse Cooperation and Collaboration |
| Cooperation and collaboration in order to carry out various projects and measures for regional development, cooperation of various private bodies and the government in developing programs to produce synergetic effects |
| 2. Prioritized Investment Looking to the New Age |
| Effective promotion of the plan through the implementation of priority programs that should be implemented in a comprehensive manner ahead of other programs, comprehensive cost reduction and responses to the dilapidation of the social infrastructure |
| 3. Demonstration of the New Hokkaido Initiative |
| Unique undertakings in order to tackle issues inherent in Hokkaido, implementation of pioneering and experimental programs that capitalize on the characteristics of Hokkaido in order to address challenges common to other regions |
|
| |
 |
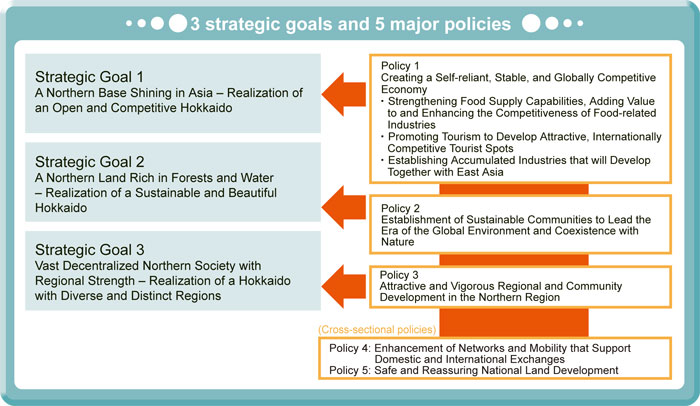
Major policies under the Plan |
| Comprehensive promotion of five major policies to achieve strategic goals |
|
| 1. |
Creating a Self-reliant, Stable, and Globally Competitive Economy |
|
|
| ・Strengthening Food Supply Capabilities, Adding Value to and Enhancing the Competitiveness of Food-related Industries |
|
| (1) |
Strengthening food supply capabilities: Strengthening capabilities to supply agricultural and marine products |
| (2) |
Securing food safety: Promotion of efforts to secure food safety through the introduction of the Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) and the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) |
| (3) |
Adding value to and enhancing the competitiveness of food-related industries: Promotion of environmentally friendly farming practices and plant breeding as well as the development of new techniques, the development and dissemination of various food products, the establishment of new food brands, the establishment of overseas market development functions, etc. |
|
| ・Promoting Tourism to Develop Attractive, Internationally Competitive Tourist Spots |
|
| (1) |
Creating attractive, internationally competitive tourist spots: Protection, cultivation and development of tourism resources attractive
to tourists from both home and abroad, the facilitation of various projects
and programs initiated by local communities, such as the Scenic Byway Hokkaido project, and recruitment and training of tourist guides |
| (2) |
Promotion of the tourism industry to lead the regional economy: Creation and dissemination of new types of tourism, development and marketing of products based on local resources, and securing, fostering and improvement of the skills and abilities of managers of projects designed to develop tourist attractions |
|
|
| ・Establishing Accumulated Industries that will Develop Together with East Asia |
|
| (1) |
Promoting industrial bases by taking advantage of geographical locations: Reinforcement of international logistics functions, establishment of production bases utilizing the existing areas of industrial concentration, concentration of processing and assembly industries, and promotion of the development of the East Tomakomai area |
| (2) |
Fostering industries by capitalizing on strengths: Fostering potential growth industries, e.g. IT, biotechnology, environmental and energy-related industries; fostering industries by capitalizing on forest resources |
| (3) |
Improving conditions for industrial development: Revitalization of local knowledge bases, creation of an environment for continued R&D activities; improvement of an employment environment for young people |
|
| |
| 2. |
Establishment of Sustainable Communities to Lead the Era of the Global Environment and Coexistence with Nature |
|
|
| (1) |
Realizing a society based on the harmonious coexistence of nature and humans: Conservation of a favorable natural environment; creating distinctive
landscape befitting of Hokkaido, and space where people can come into contact
with nature; fostering an awareness that values a rich natural environment;
promoting Ainu culture, which is closely related with nature; promoting forest development according to the functions to be valued |
| (2) |
Creating a recycling-oriented society: Reduction of life cycle costs and renovation of dilapidated public facilities; recycling based on the effective use of unused waste biomass; efforts to raise people’s awareness through environmental education |
| (3) |
Achieving a low-carbon society: Promotion of the utilization and application of energy with fewer burdens on the global environment; creation of a society in which energy is used efficiently; promotion of measures to increase greenhouse gas sinks |
|
| |
| 3. |
Attractive and Vigorous Regional and Community Development in the Northern Region |
|
|
| (1) |
Creating vast regional areas and strengthening exchanges and cooperation: Improvement of accessibility in vast regional areas; promotion of advanced land utilization and the reorganization of urban structures; reinforcement of transportation, information and personal networks; practice of open regional development and pioneering programs that will serve as a model for vigorous local communities |
| (2) |
Strengthening urban functions and enhancing urban attraction: Transition toward an urban structure with intensified urban functions; improvement of the attraction and vitality of urban areas; creation of a comfortable living environment in winter; community development based on the universal design concept |
| (3) |
Striving to create a model for vibrant local communities in sparsely inhabited areas: Fostering of joint activities concerning the conservation and utilization of regional resources and local industries making use of local resources, promotion of green tourism and marine tourism; establishment of vigorous community models |
| (4) |
Creating diverse and distinctive local communities in the northern region: Promotion of wide-ranging cooperation and collaboration in executing both structural and nonstructural measures; improvement of the environment in order to realize the early return of the Northern Territories |
|
| |
| 4. |
Enhancement of Networks and Mobility that Support Domestic and International Exchanges |
|
|
| (1) |
Establishing wide-area traffic networks connected to the rest of the nation and the world: Strengthening of high-speed transportation networks; reinforcement of logistics network functions in order to enhance international competitiveness |
| (2) |
Creating regional transport infrastructures as well as information and communication infrastructures: Creation of a well-balanced inner-city transportation system; securing of mobility in response to the actual circumstances of regions; development of information and telecommunication systems, and promotion of their utilization and application |
| (3) |
Improving the reliability of transportation services in winter: Efficient implementation of snow removal and disposal, construction of avalanche prevention facilities and snowbreak forests, securing of sufficient snow-piling space and road de-icing measures; use of the ILS for landing in both directions, improvement of runways and reinforcement of snow removal systems |
|
| |
| 5. |
Safe and Reassuring National Land Development |
|
|
| (1) |
Promoting disaster prevention measures in preparation for frequently occurring natural disasters: Promotion of fundamental disaster prevention measures; promotion of disaster prevention measures in preparation
for tsunamis and earthquakes, including trench-type earthquakes occurring
near the Japan and Kuril trenches; promotion of measures to counter heavy
snowfall, as well as disaster prevention measures for cold, snowy areas |
| (2) |
Promoting comprehensive disaster prevention and mitigation measures integrating structural and nonstructural measures: Promotion of efforts to improve regional capabilities to cope with disaster risks; promotion of the development of disaster-resistant communities; reinforcement of systems to cope with various disasters, accidents, etc.; securing of an operational and business execution system in case of an emergency, e.g. large-scale disaster |
| (3) |
Promoting traffic safety measures with the aim of creating a traffic accident-free society: Introduction of intensive automotive safety measures in areas with high accident ratios; improvement of breakwaters and other outlying facilities as well as sea routes, berths and other port facilities; maintenance of the functions of basic facilities at airports as well as air navigation facilities |
|
| |
 |
|
|