The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is an inter-governmental international organization for worldwide telecommunications. It adopts international conventions and treaties regarding frequency usage (and orbital positions of geostationary satellites) both on the earth's surface and in space (satellites). Each member country must determine its own laws based on the adopted conventions and treaties. The ITU also serves many other functions, such as development of various standards to ensure interconnectivity for global telecommunications and provision of technical support for developing countries.
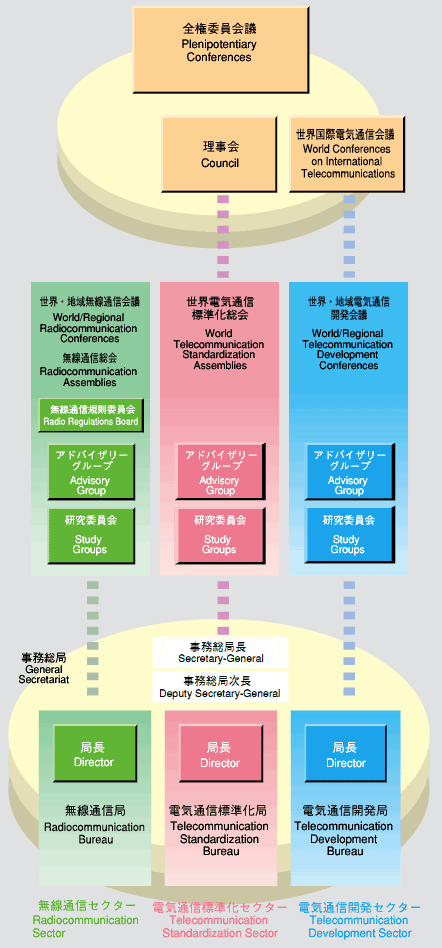
The ITU has the Plenipotentiary Conferences as its highest decision-making body, and the Council comprising 46 member countries. Sections undertaking specific operations are the Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R), the Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) and the Telecommunication Development Sector (ITU-D).
ITU's work on the Transport Information and Control Systems (TICS) was initiated when the United States proposed in 1994 that ITU-R launch studies on TICS as a new research subject. The proposal was officially approved in 1995, and Working Party (WP) 8A of Study Group (SG) 8 within ITU-R is engaged in TICS research.
 ITU : International Telecommunication Union
ITU : International Telecommunication Union
 ITU : International Telecommunication Union
ITU : International Telecommunication Union
