Once Road Communication Standard provisions are set, it is difficult to make drastic alterations. Provisions for the message interpretation function are established after thorough investigation. On the other hand, provisions for the message transfer function or protocol are not established in detail so as not to hinder the introduction of new IT technologies, which are rapidly being developed and are prone to quickly becoming out of date. The Road Communication Standard does not prescribe physical aspects that depend on transmission media, such as the shapes of connectors, or interfaces with upper application systems.
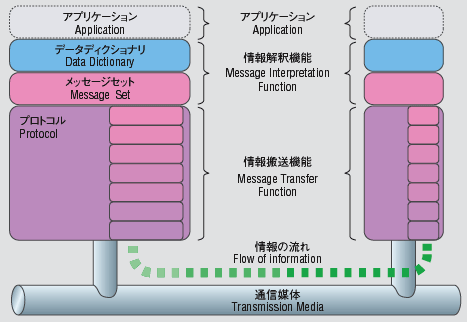 Data Dictionary Standard
Data Dictionary Standard
Just like dictionaries that people refer to in order to check the meaning of a word or a phrase while writing letters and E-mail messages, the Data Dictionary Standard defines the meaning and the utilization method of each data element, which is the minimum units of data to which all systems refer.
Message Set Standard
The Message Set Standard defines the order of saving messages in a message set, which is an information group, to correctly interpret the message, which is a set of information, in relation to the other messages. Communication is possible just by inputting a message in accordance with the standard. A message set is defined as a group of data sets, which are the minimum units of information, and a data set is a group of data elements, which are the minimum units of data.
Protocol Standard
Protocol is the rules for transmitting and receiving data among devices, and defines the type of control message, meaning, expression method, and transmission sequence (process) for transmitting and receiving data. The Road Communication Standard assumes IP-based networks, classifies each network into an upper layer, which depends on the application (Layer 3 or higher in the OSI basic reference model), and a lower layer, which depends on the transmission media (Layer 2 or lower in the OSI basic reference model), and defines a separate protocol set for each of the layer classes.
Comparison of the Road Communication Standard with a letter
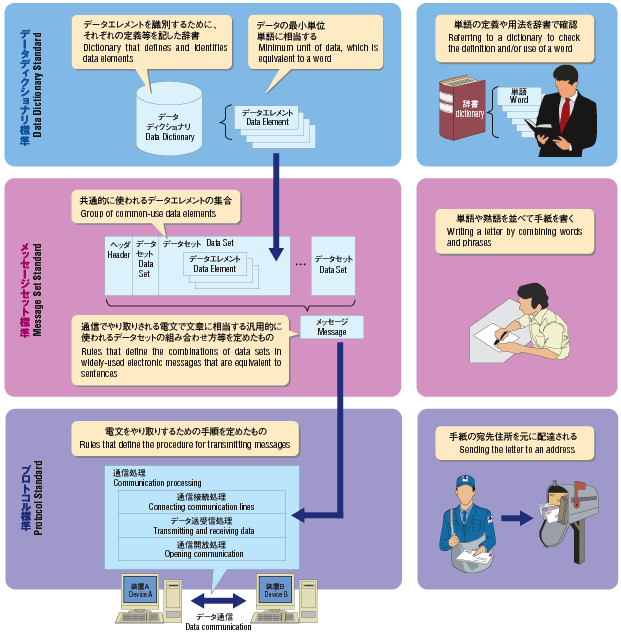
 Provisions of the Road Communication Standard
Provisions of the Road Communication Standard
 Provisions of the Road Communication Standard
Provisions of the Road Communication Standard

