Country Profile
TableCensus Summary
| Country name | People's Republic of China |
|---|---|
| Surface area | About 9,600,000 km² (about 26 times that of Japan) |
| Population | Approx. 1,376.0 million (2015) |
| Population density | 143/km² |
| Percentage of urban population | 55.6% (2015) |
| GDP | USD 10.98 trillions (2015: IMF) |
| GDP per capita | USD 7,990 (2015: IMF) |
| Percentage of employment by industry | agriculture: 33.6% industry: 30.3% services: 36.1% (2012 est.) |
| Economic growth rate (real) | 6.9% (2015: National Bureau of Statistics of China) |
(Information Updated: March 2017)
China is the fourth largest country in the world in terms of area, spanning 5,500km from north to south and 5,000 km from east to west, which shares borders with 14 other countries. Though China has the largest population in the world, liberalization and opening of the economy are progressing rapidly, and moving to a market-oriented economy is remarkable particularly in the urban areas.
At the same time as the remarkable development of the economy, disparity in economy and wealth between the urban and the rural areas and between the western inland regions and the eastern coastal regions that have been ahead in the urbanization and the economic development has become a problem.
Also, it has become a social problem that people transfered from agriculture (migrant workers) cannot have family resisters in urban areas, and have no access to the social welfare services as same as that the people registered in urban areas can access to. Urbanization of the people transfered from agriculture (migrant workers) by unifying the family registers in the rural areas and the urban areas is required.
FigureProvincial-level Administrative Divisions of China
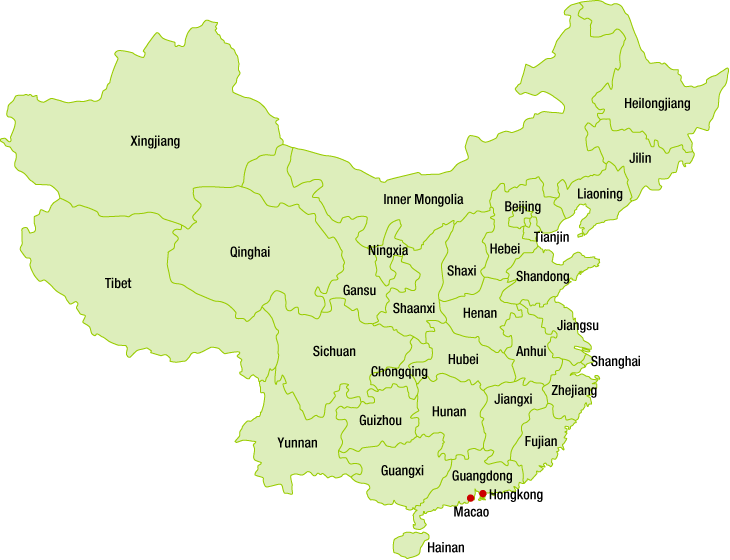
Source: Research Institute for Urban & Environmental Development, JAPAN
Relationship between the central government and the local governments
The local government system consists of four layers; Provincial level, Prefecture level, County level and Township level.
Figure:Local government system
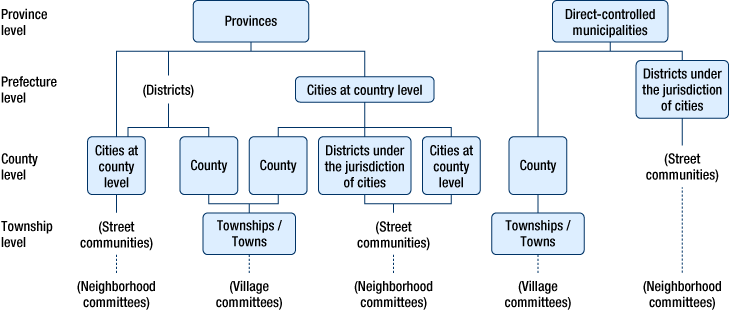
- (Note 1)
- Special Administrative Regions and Autonomous Regions are omitted.
- (Note 2)
- This is a basic figure that shows typical examples, and there may be street communities, townships and towns under the county level cities or the districts of the jurisdictions cities.
- (Note 3)
- The neighborhood committee or the village committee is a resident's autonomy organization that provides necessary administrative services under the guidance of the county level government.
Source: Local Authorities for International Relations Forum, general incorporated foundation,
“Overview of Chinese Administrative Systems” (June 2000 Edition)
System of Spatial Policy
The spacial policy in China is related to three planning systems; the socioeconomic development plans, the national spatial plans (land use plans), and the urban and rural plans.
Socioeconomic development plans are created in each of the four administrative levels of the national, the provincial, the prefecture, and the county level.
The national spatial plans (land use plans) are created in each of the five levels of the national, the provincial, the prefecture level, the county, and the township level.
The urban and rural plans consist of the urban system plans, the urban plans, the town plans, the township plans, and the village plans. The urban system plans are created in each of the six levels of the national, the provincial, the prefecture, the county, the township,and the village level.
Figure:System of Spatial Policy in China
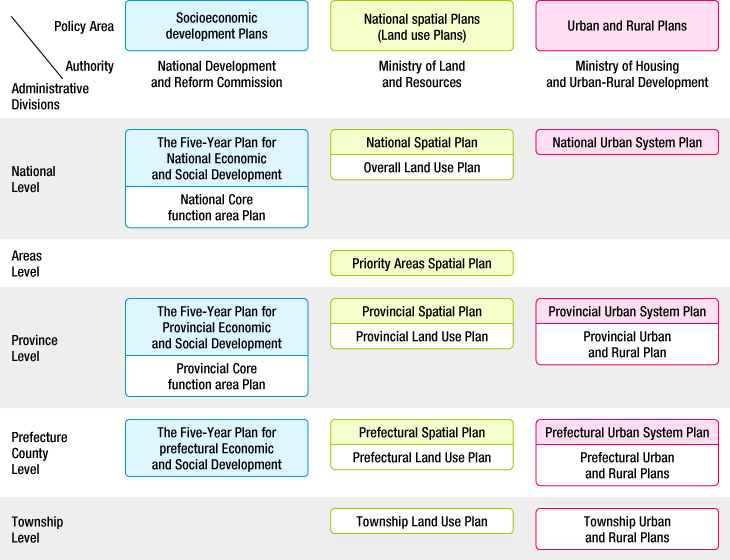
- Note:
- Strategic zones have not been specified yet, and they will be specified focusing on the viewpoint of effective utilization promotion of resources and mineral products.
The urban plans for the direct-controlled municipalities, the country level cities, the county level cities, the towns include the master plan, the control type detailed plans, and the construction type detailed plans.
Source: From “Study Group on Spacial Policy of Foreign Countries” with field study, etc.
Major Authorities Relating to Spatial Policy
| Program name or administrative field | Organizations | Webpage |
|---|---|---|
| The Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development (11th) |
National Development and Reform Commission | http://www.sdpc.gov.cn/ |
| National Spatial Plan, Overall Land Use Plan |
Ministry of Land and Resources | http://www.mlr.gov.cn/ |
| Urban System Plan, Urban and Rural Plan |
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development | http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/ |
The Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development
The basic national development policy for China is embodied in the Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development. This plan mainly shows the distribution of significant construction projects and production capacity, as well as the targets and directions of the national economic development.
After the People's Republic of China founding in 1949 (the First Five-Year Plan was developed in 1953), the regional development policy has been mainly focusing on the two points of efficiency and equity, it is roughly divided into following 3 stages. In the first stage, from the initial stage of founding to the Reform & Opening up, the strategy was made focusing on the balanced national development, in the second stage, from the Reform & Opening up to the mid-1990s (20th century), the strategy was mainly focusing on the non-equilibrium development, and in the third stage of the development, after the mid-1990s, the policy has turned into the balanced national development and the coordinated development of the regional economy.
The 13th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development (commonly called “The thirteen Five”) that is for 2016 to 2020, has been approved by the 12th National People's Congress (it corresponds to the National Assembly in China) held in March 2016.
Since the 13th Five-Year Plan is nearly the same period as the end timing of the first 100 years (until 2020) in which “Full completion of the well-off society” is targeted, the period of the plan has been positioned as a “stage that determines the outcome of the overall completion of the the well-off society” and the plan shows urgency for achieving the targets.
“Full completion of the well-off society” is the first half of the long-term consul goals that Chinese Communist Party claims “two of 100 years” (Chinese Communist Party founding 100 years and the People's Republic of China founding 100 years).
In the edition I, the main goals and development philosophy, the great development philosophies that include the innovative development (Innovation), the coordinated development, the green development (Green and low-carbon society), the open development, the shared development (Sharing), are listed and aiming people's overall development.
As matters related to the spatial policy, “Promotion of agriculture modernization”, “Construction of modern infrastructure network”, “Promotion of the new urbanization”, “promotion of coordinated regional development”, “Acceleration of the ecological environment improvement” are going to be carried out. In the “Promotion of the new urbanization”, “Acceleration of urbanization of the people transfered from agriculture” including the promotion of the family register system reform, “Optimization of the spatial arrangement and the urban forms” including Two-horizontal Three-vertical Urbanization Strategy, “Construction of balanced livable city with harmony”, “Improvement of housing supply system”, and “Promotion of urban and rural coordinated development” are going to be carried out. Also, as a part of “Acceleration of the ecological environment improvement”, “Promotion of core function area setting” is listed.
Figure:Urban group spatial distribution diagram (the 13th Five-Year Plan)
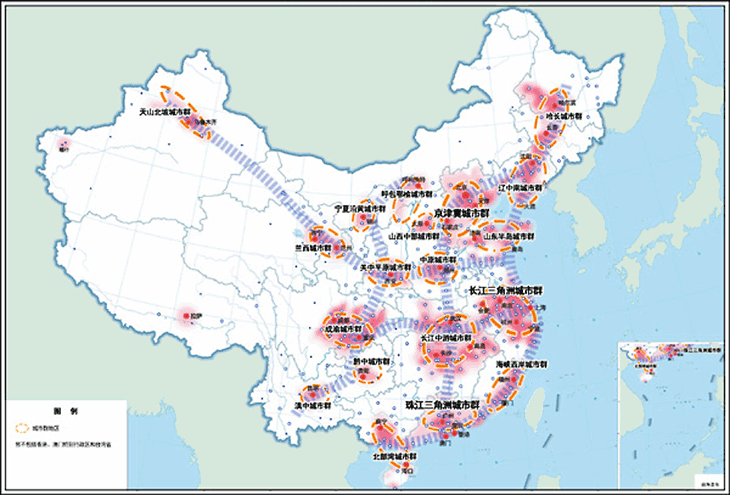
Source: The 13th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development Edition 8, Chapter 33, Section 1
Considering “the Land Bridge (Eurasian Transcontinental Railroad) route” and “the route along the Yangtze River” as the two horizontal axes, and considering “the coastal route”, “Beijing-Harbin and Beijing-Guangzhou route” and “the Baotou-Kunming route” as the three vertical axes, the urbanization Strategy called “Two-horizontal Three-vertical” in which a few cities along the axis are set as the development cores is going to be carried out. In addition, the plan improves the economic strength and the population absorption capacity of small and medium-sized cities to avoid the excessive concentration of economic functions to the extra-large cities.
Spatial Plans on National and Regional Levels
The spatial plans in China consist of the national spatial plans (land use plans) and the urban and rural plans.
One of the arterial spatial plans is the National Spatial Plan that is under the control of the Ministry of Land and Resources. This plan includes the safe construction of the national land ecosystem, the optimal allocation of the national land resources, the rational structure of the national space, the ability improvement for security of the energy resources, the promotion of the general preservation of the national land, the security of implementing the national spatial plan, etc. The first conference of Instructing Group of Establishing the Outline of National Spatial Plan was held in September 2010 and the conference passed “Method of Establishing the Outline of National Spatial Plan” and “First Half of the Study for the Outline of National Spatial Plan 2011-2030”. After three years' formulation, the Outline of National Spatial Plan 2011-2030 was finally completed in October 2013, and submitted to the State Council for approval.
The scope of the land use (spatial) planning system consists of the overall land use plan (master plan), the sector specific land use plans, and the detailed land use plans. The overall land use plans (master plans) formulated for the entire country and each provincial region correspond to the national and regional level plans, and they are the statutory plans based on the Land Management Law. The third phase overall land use plans were formulated in October 2007. The overall land use plans dictate the general allocation of the land resources, and development, use, improvement, and conservation of the land resources as strategic plans. The Land Management Law stipulates that the master plans of the lower administrative bodies are to follow those of the higher administrative bodies.
In the system of the urban and rural plans, The urban system plans formulated for the entire country and each provincial region correspond to the national and regional plans. These are statutory plans based on the Urban and Rural Planning Law. The Urban System Plans are related to the development of specific areas (the entire country and each provincial region). As development in the urban area gives great impact to the region-wide development, the Urban System Plans intend to develop the regional economic societies and develop and allocate the corresponding urban areas. The National Urban System Plan is positioned as a plan to guide formulation of the Provincial Urban System Plans and the Urban Plans (Urban Master Plans).
System overview of the metropolitan area plan
53 state strategic regional plans have been approved by the country till April 2014. The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the Yangtze Delta region, and the Pearl River Delta region are called the three largest metropolitan areas in China. In the 13th Five-Year Plan for the national economic and social development, the edition 8, Chapter 38 shows “Promotion of the coordinated development in Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei”.
The National Development and Reform Commission started the preparatory work for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan planning in 2004. This plan was submitted to the State Council for approval in 2010, then approved in 2015 and has been put into practice.
The Yangtze Delta Plan started in 2004, and after 2 years' preliminary survey and 4 years' formulation, it was officially approved by the State Council in May 2010 and has already been put into practice.
The Pearl River Delta Plan deals with only one province (Guangdong). The Pearl River Delta reform and development plan summary is completed with cooperation of the Guangdong government and the Ministry of Urban-Rural construction, and got approved in December 2008. In the council for the promotion of Pearl River Delta “Nine-Year long-term” work held in May 2014, the Guangdong province government announced that “We must execute the plan related to the entire Pearl River Deltain to carry out the Pearl River Delta development as a world-class city cluster”. In July 2014 the formulation of the Pearl River Delta Master Plan which was added improvements to the Pearl River Delta reform and development plan summary was formally initiated in order to upgrade the Outline of Pearl River Delta Reform and Development Plan.
National New Urbanization Plan
In the Central Rural Work Conference held in December 2013, policies for modernization of rural areas and for new urbanization were announced in addition to the importance of the Three Rural Issues, and ensuring the food security (ensuring an arable land area at least 1.8 billion mu (approx. 1.2 million km²)), etc.
This plan is aimed at accelerating rural urbanization to promote securement of the national food security and increase of the peasant's income.
“Urbanization should be promoted in proactive, appropriate and consistent manner in order to make agricultural population of 100 million people residing continuously in urban area entrenched in the area by 2020, reform low-income housing zone and villages (or towns) within the cities and resolve urbanization problem of 100 million people in the central and west area in order to actualize: mutual complement of new urbanization and rural modernization, promote construction of new rural areas by emphasizing each of the characters and strive for the better living of the wide range of mass peasant”. (People's Daily; December 25, 2013).
While the urbanization has remarkably been success, a lot of problems such as formation of double structure consisting of the urban residents and the migrant farmers (migrant workers) and etc. have been accumulated and begun to be revealed. With this background, the need to shift from the conventional procedure focusing on the hardware aspect construction such as the infrastructure to “new urbanization” focusing on the software aspect construction such as the system has been widely recognized. “National New Urbanization Plan (2014-2020)” that incorporates the government policy to aim for the above was announced by the Chinese Communist Party Central and the State Council in March 2014.
This “Plan” states promotion of “new urbanization” and the basic policies are following 5 items.
- People-oriented, fair profit sharing
- Balanced development of urbanization, agricultural modernization, computerization and industrialization, and integration of urban and rural areas
- Optimization, consolidation, and streamlining of the allocation
- Promotion of ecological civilization, green and low-carbon society
- Culture handing down and manifestation of city individuality
Source: “New Urbanization” Chi Hung KWAN RIETI (Research Institute of Economy, Trade and Industry) July 11, 2014 posted
These directions listed in the “National New Urbanization Plan” were incorporated in the 13th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development Edition 8 "Promotion of the new urbanization", and taken over.
One Belt and One Road
One Belt and One Road (OBOR) is the abbreviation of the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. China's chairman Xi Jinping addressed the strategic idea of constructing both the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road when he was visiting the Central Asian and Southeastern Asian countries in September 2013.
The One Belt And One Road strategy attempts to construct a mutually linking transnational economic system mainly through development of ground / sea, and construction of transportation infrastructure. The key collaboration in this strategy would be lying on the connection and communication of policy, facility, trade, capital, morale and so on.
The Silk Road Economic Belt strategy comprises the integration of the Southeastern Asian economy and the Northeastern Asian economy. They finally merge together and direct toward Europe, and it is expected to promote Eurasia's economic integration. In addition, the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road strategy tends to connect the European, Asian and African continents through seaway, and construct a marine and overland closed circle along with the Silk Road Economic Belt strategy.
Through constructing the extensive communicating and collaborative mechanism with 4 billion people of nearly 60 countries, China can obtain the external resources and provide its domestic products, capital, assistive technologies. By January 2015, the One Belt And One Road strategy has received 60 countries' supportive participation.
In February 2015, the Promoting “One Belt and One Road” Construction Work Conference was held in Beijing, in which the procedure of key activities and tasks in the next period to promote the One Belt and One Road strategy was declared. And the information that the One Belt and One Road Plan has already been approved and would be released soon was given. More than two-third of the 28 provinces (which had already held the Local Two Conferences by February 5, 2015) are under formulation of their own relevant plans to follow the nation-level One Belt And One Road strategy.
In the 13th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development Edition 4 Chapter 51 states the promotion of the One Belt and One Road Plan.
(Information Updated: March 2016)
