Country Profile
New Zealand, which lies 2,250km southeast of Australian Continent, is composed of two large islands (North Island and South Island) and small islands nearby. It belongs to a part of circum-Pacific seismic belt and is a mountainous country with about 75% of its national land at more than 200m above sea.
New Zealand was found by Maoris, the receiver of Polynesian culture. In 1642 New Zealand was visited by Tasman from Netherlands which made him the first European to visit this land, then in 1796 it was explored by a British explorer Cook which led New Zealand to become a British Crown Colony in 1840. After becoming a dominion within the British Empire in 1907, it became independent as one of the Commonwealth of Nations in 1947.
Population of the country is 4.44 million (2012) of which 3.39 million is in North Island and 1.04 million in South Island (estimation of Statistics New Zealand in 2012). Ethnic composition is; European 56.8%, Asian 8%, indigenous people Maori 7.4%, South Pacific Islands 4.6%, mixed race 9.7%, others 13.7% (Population Census; 2006)
TableNew Zealand fast facts
| Country Name | New Zealand |
|---|---|
| Surface Area | 270,534 km² (about 75% of that of Japan) |
| Population | Approx. 4.24 million (end of 2012: estimation by Statistics New Zealand) |
| Population Density | 16/km² |
| Percentage of Urban Population | 86.3% (2015) |
| GDP | USD 172.3 billion (2016: IMF) |
| GDP per capita | USD 306.6 (2016: IMF) |
| Percentage of Employment by Industry | agriculture: 4.2% industry: 26.5% services: 69.2% (2016 est.) |
| GDP Growth Rate (real) | 1.4% (2010-2011), 2.5% (2011-2012) 2.3% (2012-2013), 2.8% (2013-2014) 3.6% (2014-2015), 2.4% (2015-2016) |
(Information Updated: March 2017)
Local Government System of New Zealand
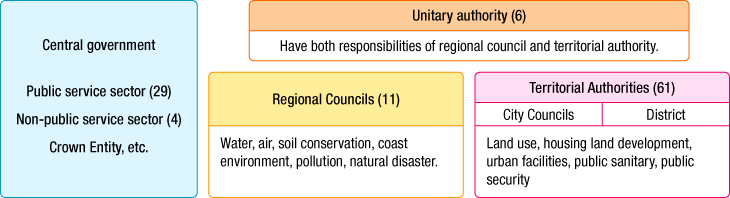
The political system of New Zealand is constitutional monarchy having the queen of UK as head of the state employing parliamentary system. Local government system consists of one regional council, 61 territorial authorities and 6 unitary authorities.
Authority of regional council is not always extensive. Regional Council is more likely to have the character of regulatory agency and its main role is to deal with water, air, soil conservation, coast environment, pollution, natural disaster, etc. Regional Councilors are publicly elected and the chairman is mutually elected by the councilors. On the other hand, power of territorial authority have a wide range of fields including land use, housing land development, urban facilities, public sanitary and public security. Mayor and councilor of territorial authorities are elected by direct election.
Figure:Local Administration System and Government Organization of New Zealand
Major Authorities Relating to Spatial Policy
| Name/Field of the plan or policy | Authority | Web Page |
|---|---|---|
| National Policy Statements National Environmental Standards Urban Plan |
Ministry for the Environment | http://www.mfe.govt.nz/index.html |
| National Infrastructure Plan | National Infrastructure Unit, The Treasury | http://www.infrastructure.govt.nz/ |
| Government Policy Statement on Land Transport Funding New Zealand Transport Strategy |
Ministry of Transport | http://www.transport.govt.nz/ |
| National Land Transport Programme | NZ Transport Agency | http://www.nzta.govt.nz/index.html |
| Regional Economic Development (coordination and management of policy challenges) Regional Economic Activity Report |
Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment | http://www.mbie.govt.nz/ |
Plans/Policies related to National Land and Regional Development
<physical /Spatial planning>
Urban planning system of New Zealand consists of following planning documents which are stipulated in Resource Management Act (1991), Local Government Act (2002) and Land Transport Management Amendment Act (2003).
| Acts stipulating the formulator of the document | Central Government | Regional Council | Territorial Authority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Management Act (RMA; 1991) |
|
|
|
| Local Government Act (LGA; 2002) |
|
||
| Land Transport Management Amendment Act 2013 (LTMA) |
|
|
|
- *Documents for electric power transmission, electric generation using renewable resources, policies for coastal area and management of land water (these are already published) and documents for urban design and native biodiversity which are now being established.
<Regional policy>
Each regional council is encouraged to establish Regional Economic Development Strategy.
Trend related to national land policy and spatial planning in recent years
<National Land Policy>
- General plan for the whole national land does not exist.
- National Infrastructure Unit which was established within The Treasury in 2009 has started formulating National Infrastructure Plan including the fields of transport, communication, energy, water supply, waterworks and social infrastructure. Long-term vision for 20 years targeting 2030 was established in 2011 to set a framework of infrastructure development. National Infrastructure Plan aims at long-termed and scheduled way of using fund. Based on the activities since 2010, they are planning to formulate a reliable plan in 2015.
<Physical /Spatial planning>
- Following the establishment of Auckland Plan which is the document based on the concept of new "spatial plan", effectiveness of establishing spatial plans for the areas out of Auckland has been re-examined (especially of the plans related to national funding for infrastructure development). Also it has been discussed about the position of "spatial plan" among the national plans (including the idea of National Spatial Plan).
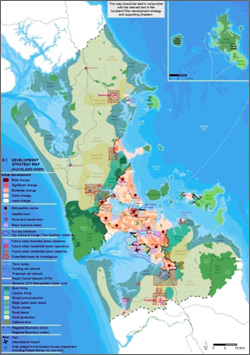
Trend in Metropolitan Area (Auckland)
<Establishment of Auckland Plan which is the first spatial plan and also the plan having linkage with financial plan.>
- Auckland City became a Unitary Authority in November 1, 2010, by merging one Regional Council and seven Territorial Authority.
- It is expected in Local Government (Auckland Council) Act 2009 that Auckland Plan will contribute to social, economic, environmental and cultural well-being of Auckland through Long-term Strategy Contributing to Efficient and Comprehensive Growth and Development of Auckland (20-30 years plan).
- Auckland Plan is composed of Unitary Plan which states policies and rules to implement the plan, Place-based Plans, Core strategies and Long Term Plan.
- After four stages starting from the first workshop followed by Result Papers of Free Discussion, Draft Auckland Plan and then Final Auckland Plan, at last the final plan was published in March 2012 (it took 17 months to be established).
- Auckland Plan is the first spatial plan in New Zealand and as it is linked with financial plan it has been attracting much interest of other local governments.
<Outcome to be reached and development strategy>
- Auckland Plan is formulated based on the vision of current Mayor; "Making Auckland the most comfortable city in the world to live."
- Population growth is expected to be one million within 30 years and 400 thousand housings are planned to be constructed (current population is approx. 1.5million).
- 60 % of one million is expected to be natural increase and inflow from other areas in the country while 40% is estimated to be inflow from overseas.
- The plan will be heading for high-quality and compact development based on the concept of "70 for inside of Metropolitan Urban Limit and 40 for outside of Metropolitan Urban Limit (new development)" in 2010.
Regional Economic Development
<Formulation of The Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment>
- In July 2012, The Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE) was formulated by integrating two ministries and two departments. Having Ministry of Economic Development and Ministry of Science and Innovation as the cores the new ministry was made up by bringing together Department of Labour under Ministry of Employment and Labour and Department of Building and Housing under Ministry for the Environment as well.
- The principal interest of MBIE is to make political advices for groups of regions or cities (mostly Auckland and Christchurch) to maximize their contribution towards national development and prosperity.
- MBIE governs the management of Auckland Policy Office, the authority dealing with enhancing international competitiveness of Auckland, which is the alliance of related ministries of the central government established in 2005. Also MBIE implemented Core Cities Research targeting six largest cities such as Auckland, Christchurch, and others.
- At the same time MBIE started to deal with, upon the cooperation with Auckland Policy Office, regional development policy for the areas out of metropolitan areas and policy to enable each region develop by utilizing their specific characters, both of which are carried out based on regional economic analysis which was implemented by dividing the country into 16 areas. In seeking to outgrow the traditional approach depending on subsidies and transfer to smart and specified regional policy like what is implemented in OECD and EU countries, New Zealand is making efforts in technical and skill development adapted to regional characteristics.
Policies for disadvantaged areas (policies for the regions of primary industry and Maoris)
- Explicit policy does not exist in New Zealand which specifies "disadvantaged areas".
- However, at the areas whose industry is centered by primary industry such as agriculture, forestry and fishery, income level is low compared to that of urban areas and also population is sparse which can be explained as depopulated areas. Moreover, the indigenous people Maori possess a great deal of interest in agricultural land and fishery and as they are also the bearer of those industries, their habitation area is facing the same problem with other agricultural, forestry and fishery areas.
- Primary industry is the important industry in New Zealand which underpins the country's economy as it can be seen in current export of which two thirds is covered by agricultural products. After the joining in of United Kingdom to European Communities in 1973 which extinguished compensation of sales outlets of New Zealand's agricultural products, the government implemented compensation for farm household income and took various other measures but all such policies had been abolished among administrative and financial reform since 1984. However, R&D for efficient farm management and aid for research and development had been maintained which have been making results in creating agriculture, forestry and fishery industry with international competitiveness. Currently there are no special support or tax benefits.
- Measures with emphasis on management innovation and research development are implemented by making use of cooperative fund of public and private sectors such as Sustainable Farming Fund (SFF), Fund for Aquaculture Reform, Irrigation Acceleration Fund, Primary Growth Partnership (PGP), etc.
- As for the Maoris, given the state that they have less knowledge and skills related to utilization of land resource and there is no know-how of management, the government takes measures from the view of promoting efficient use of land and increasing productivity by showing preliminary calculation of management models, making model-farm to transmit and familiarize the image of management, etc.
(Information Updated: March 2014)