Country Profile
The Republic of Korea covers almost half of the Korean Peninsula and is about one fourth of the size of Japan. Its geographical features are similar to those of Japan in its mountainous feature: about 70% of the country is covered by mountainous terrain.
The end of Second World War saw the stationing of Soviet and U.S. troops on the north and south sides of the 38th parallel, which marked the beginning of a process that split the country into two. In August of 1948 a government was established in the south (the Republic of Korea). The following month saw the formation of a separate government in the north (the Democratic People's Republic of Korea).
During the period of economic growth, despite the implementation of Comprehensive National Plan and policies to prevent overconcentration in the capital, concentration to the capital area continued which led to traffic problems, rapid increase of housing prices and congestion problem in the capital area such as environmental problems. Also, disparities between the regions and between the levels of urban hierarchy remained, thus regional deviation in major development indicators had been an issue to be solved. In the 2000s, climate change worsened internationally, and domestically, comprehensive strategy for national land and urban area taking in account environmental and economic aspects is required due to the declining birth rate and the aging of society and change in economic structure.
TableKorea fast facts
| Country name | Republic of Korea |
|---|---|
| Surface area | About 100,000 km² (roughly 45% of the Korean Peninsula; quarter the size of Japan) |
| Population | About 51.50 million (2015.12) |
| Population density | 515/km² |
| Percentage of urban population | 82.5% (2015) |
| GDP (nominal) | USD 1,417,000 million dollars (2014) |
| GNI per capita | USD 22,460 (2007), USD 22,850 (2008) USD 21,090 (2009), USD 21,320 (2010) USD 22,620 (2012), USD 22,640 (2013) USD 27,090 (2014) (Ministry of Strategy and Finance) |
| Percentage of employment by industry | agriculture: 2.3% industry: 37.6% services: 60.2% (2016 est.) |
| GDP growth rate | 5.5% (2007), 2.8% (2008), 0.7% (2009) 6.5% (2010), 3.7% (2011), 2.3% (2012) 2.4% (2013), 3.7% (2014), 2.6% (2015) (World Bank) |
(Information Updated: March 2017)
FigureMap of Korea
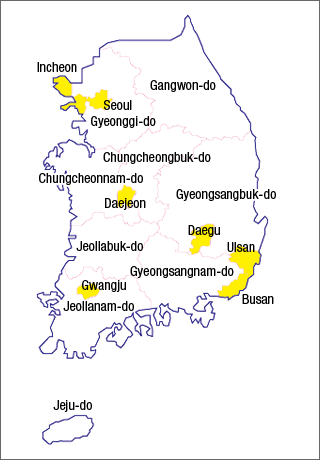
Sources: Research Institute for Urban & Environmental Development, Japan
Local Governments and Spatial Planning System
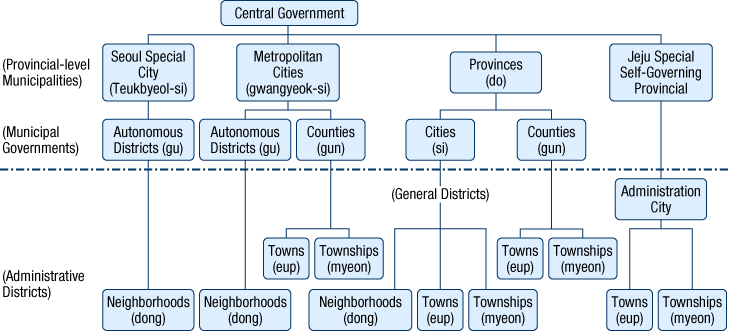
Local governments can be divided into provincial-level municipalities, city-level municipalities, and lower administrative units.
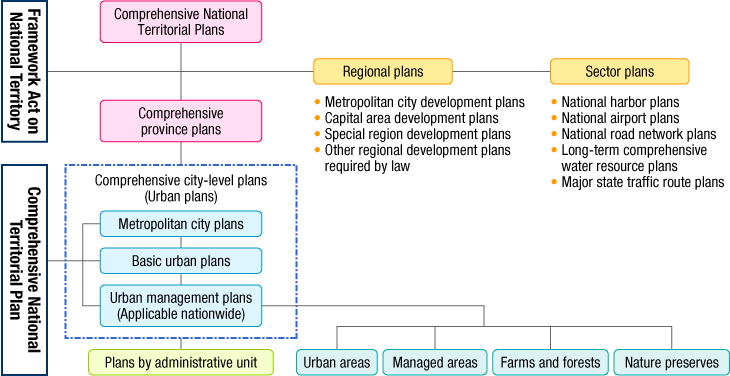
In terms of planning systems related to spatial policy, Korea has a system of Five-Year Plans for Balanced National Development, which consists of socioeconomic development plans, and Comprehensive National Territorial Plans, which amount to spatial plans.
The national land and urban planning system is unified based on Framework Act on National Territory and National Territorial Planning Act (Plan on Planning and Use of National Territory). Comprehensive National Territorial Plan will be established based on Framework Act on National Territory, and Wide-area Urban Plans and Urban Plans will be established based on National Territorial Planning Act. The structure of the planning system is "Comprehensive National Territorial Plan - Wide-area Urban Plan - Urban Plan", of which the lower-level plan is to follow the upper-level plan.
In this planning system, Comprehensive National Territorial Plan which was organized upon the enactment of Framework Act on National Territory in 2002 exists in parallel with Comprehensive Provincial Plan and Comprehensive City-level Plan. At the same time, sectoral plans such as National Transport Network Plan, Housing Plan, etc. and regional plans such as Wide-area Development Plan, Capital City Development Plan, etc. are made to correspond with this plan. Wide-area Urban Plan is the upper-level plan which sets out the planning direction of inter-city plans of more than two neighboring cities. As of 2014, 12 inter-city areas including capital area, Busan area, Machangjin (馬昌鎭) area (former Masan City, Changwon City and Jinhae City) are preparing for this kind of plan.
Source: "2008 Annual report on the planning and use of national territory", Ministry of Land, Transport, and Maritime Affairs, Korea
Governmental Organizations in charge of Territorial Development Policy
| Program name or administrative field |
Organizations | Webpage |
|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive National Territorial Plan, Capital Area Development Plan |
Ministry of Land Infrastructure and Transport | http://www.molit.go.kr/portal.do |
| Promotion of enterprise city policy | Ministry of Land Infrastructure and Transport | http://www.molit.go.kr/portal.do |
| Five-year plan for Regional Development | Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy | http://www.motie.go.kr/ |
Outline of planning system for balanced national development
Since 1962, Korea has established five-year plan for economic development as an upper level plan for national socio-economic development, which counted up to the 7th Plan.
Replacing this, Roh Moo-hyun administration established Special Act for Balanced National Development and formulated Five-Year Plan for Balanced National Development (2004-2008).
The act was amended under Lee Myung-bak administration (2009-2013) in order to contribute to balanced regional development by improving regional competitiveness and living standard through development that suits regional character and promoting inter-regional cooperation and partnership. The administration also set up three specific zones (basic living zone, wide-area economic zone and super-wide living zone) and established "Five-year Plan for Balanced Regional Development".
Park Geun-hye administration (2014- ), in the finalized Five-year Plan for Regional Development, sets out improvement of regional inhabitants' quality of life and creation of employment as two major goals. In contrast with the past regional plans which were proposed and implemented under the initiative of the central government, regional plan of Park administration focuses on the concept of "region-customized" and encourages local governments and local residents take initiative of regional development by themselves. Therefore the central and local government prepared the plan cooperatively which was also different from the former plan. The outline of the plan will be summarized in the following five issues;
- (1) Vitalization of regional living areas
- (2) Creation of regional employment
- (3) Improvement of educational environment
- (4) Flourishing of regional culture
- (5) Welfare and medical services without blind spots
Upon this plan 56 regions is designated as "living areas of happiness", and enhancement of infrastructure such as enhancement of water and sewerage system in agricultural and fishery villages and increase of neighborhood parks will be promoted, and also funds for economic development is going to be injected for projects such as development of town enterprises, promotion of regional employment by creative industry, etc.
Comprehensive National Territorial Plans
According to Comprehensive National Territorial Development Plan Act, Comprehensive National Territorial Development Plan has been established in Korea at an interval of about a decade since the 1st Plan (1972-1981) up to the 3rd Plan.
The act was revised as Framework Act on National Territory (2002) and the name of the plan was changed to Comprehensive National Territorial Plan and the 4th Comprehensive National Territorial Plan (2000-2020) was established.
Its planning system is characterized by its formulation. In concrete, it is formulated by layered structure (Comprehensive National Territorial Plan - Comprehensive Provincial Plan - Comprehensive City-level Plan) with Regional Plan for specific regions and Sector Plan for specific sectors. It is also characteristic that urban plans of respective cities/counties (apply to the whole administrative area which makes difference with those in Japan) which are established based on Plan for Planning and Use of National Land are provided as Comprehensive City-level Plans.
Comprehensive National Territorial Plan is revised once every five years and currently being exercised is the 4th Comprehensive National Territorial Plan Corrective Plan (2011-2020). The plan has a vision of "Global Green National Land for Korea's another jumping-up", sets out four objectives --- comprehensive national land with competitiveness, sustainable green national land, attractive national land with dignity, and national land open to the world--- and announces the promoted strategies, namely, "Strengthen regional specialization and wide-area partnership to enhance competitiveness of national land", "Create nature-friendly and safety national space", "Create comfortable and cultural urban/housing environment", "Formulate integrated network of green transportation and national land information", "Formulate land foundation of newly growing maritime nation open to the world" and "Formulate national land management foundation beyond national boundaries". Notable factors of the plan are that it (1)shifted over from mathematical sense of balance to regional development strategy that focuses on regional competitiveness, (2)adopted green growth strategy, and (3)set out objectives to strengthen co-development within regions and dignity and openness of national land.
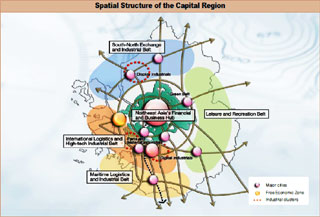
Metropolitan Planning System (Spatial structure of the Capital region)
Pursuant to Article 4 of the 1982 Capital Region Readjustment Planning Act, the Capital Area Development Plan is a comprehensive, long-term plan that sets forth the fundamental principles for the basic direction for development or improvement projects in the capital, the physical distribution of people and industries, and the construction of facilities in the area. The current plan is the third of its kind (2006-2020).
The Capital Area Development Plan takes precedent over other laws and regulations in place in the area involving land use plans and various development plans. In fact, it forms the basis of those laws and regulations. The Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs develops a draft, submits it to the Capital Area Development Plan Committee (chaired by the Prime Minister), which deliberates and finalizes it.
The Capital Region Readjustment Planning Act contains regulations for the construction of universities, factories, public complexes, and other large buildings, regulations on the development of land for industrial and housing purposes, and location rules set out according to specific districts in the area (e.g. those which have measures in place to curb overcrowding, those with measures to manage growth, and nature preserves).
International Perspectives in the Current Comprehensive National Territorial Plan
The 4th Comprehensive National Territorial Plan Corrective Plan (2011-2020) sets out its policy to create a belt composed of east coast area, west coast area and south coast area as "super wide-area development zone" and intensively develop it as a strategic growth axis to expand into continent and oceans, and that is to make use of geopolitical advantage of Korean Peninsula.
Moreover, it states its objectives to strengthen global gateway function of ports and airports which include; specializing hub ports within each wide-area economic zone, strengthening North East Asia Port Alliance, enhancing air liberalization, strengthening hub function of Incheon International Airport, etc.
The plan sets out, in view of ultralong-term, to promote international cooperation for establishing railway transport and logistics system to enable expanding into Asia and Europe and for connecting the missing link in Asian Highway, through connecting Korean Peninsula Railway Network with Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR) and Trans-China Railway (TCR).
In addition, it presents direction to promote cooperation within cross-border regional development in Northeast Asia & ASEAN area through exploring and promoting joint project, expanding institutional cooperation within involved countries, etc.
- InnoCity
- Article 18 of Special Act for Balanced National Development sets an assumption that the nation will take measures to relocate government ministries/institutions to local areas and 157 government ministries/institutions were designated based on this article. To treat those that move to sites out of Sejong city, "Special Act for Constructing and Supporting InnoCity (Innovation City) in Consequence of Government Ministries' Relocation" was established in January 2007.
- InnoCity aims at performing centripetal role of regional innovation by relocating government ministries/institutions collectively from metropolitan area and developing new environment with fine environment to settle for ministries/institutions, universities, research institutions and enterprises which will enable outstanding human resources take root in local areas. The project will bring construction of total 10 cities in each provincial-level municipality (excluding metropolitan area and Sejong City).
- The Act provides for; assistance for relocating ministry/institution and its staff; measures on disposal and use of moved out site; establishment of special account; procedure of urban development; etc.
- Period of the project is 2007-2030. Stage 1 (2007-12) is the stage for relocated governmental ministries/institutions to settle; Stage 2(2013-20) is the stage for industry, academia and research bodies to settle; Stage 3 (2021-31) is the stage for innovation to diffuse. Planned staff of relocated ministry/institution and related companies is 2,500-4,000 in each city and planned induced population is 15,000-25,000.
- Province-level Municipalities in Korea consists of Seoul Special City, 6 Metropolitan Cities and 9 Provinces. Municipal Governments consists of 163 cities and counties.
- Sejong Special Autonomous City
- Sejong Special Autonomous City has its construction basis on the Act for Construction of Sejong Special Autonomous City which was enacted in 2010 after the Special Act on the Construction of the New Administrative Capital was decided unconstitutional at the constitutional court in 2004. This enactment resulted in creation of Sejong City, the first special autonomous city in South Korea, in July 1, 2012. Sejong City is positively promoting measures to invite high-tech industry and universities, to formulate worldwidelevel education, culture and welfare infrastructure and to develop high-tech information city in order to secure self-sufficiency and to provide adequate living environment for the citizens. As for public organizations, 12 central administrative bodies including Office of the Prime Minister completed relocation in 2012, followed by 18 bodies in 2013 and 6 bodies in 2014.
- Self-Sustaining City
- Self-Sustaining City is a city that focuses on the establishment of industries and economic activities which is developed at the initiative of private companies. The companies develop necessary sites by themselves to maximize efficiency and cooperation among related industries, for example production and research development industries, and at the same time, the city will be provided with self-sufficient multiple functions for inhabitants including housing, education and health care. Special Act for Developing Self-Sustaining City was enacted in 2004 and six areas were designated as model project areas in August 2005, of which five cities --- Taean, Chungju, Wonju, Muan and Yeongam/Haenam --- have reached final decision until 2014. Detail of Special Act for Self-Sustaining City was amended in 2011 and 2012.
(Information Updated: March 2015)